A key decision for effective packet analysis is where to position a packet sniffer to appropriately capture the data. This is most often referred to by packet analysts as sniffing the wire,tapping the network, or tapping into the wire. Simply put, this is the process of placing a packet sniffer on a networkin the correct physical location.
Unfortunately, sniffing packets is not as simple as plugging a laptop intoa network port and capturing traffic. In fact, it is sometimes more difficult toplace a packet sniffer on a network’s cabling system than it is to actually analyzethe packets.
The challenge with sniffer placement is that a large variety of networkinghardware is used to connect devices. Figure 2-1 illustrates a typical situation.Because the three main devices on a modern network (hubs, switches, androuters) each handles traffic differently, you must be very aware of the physicalsetup of the network you are analyzing.
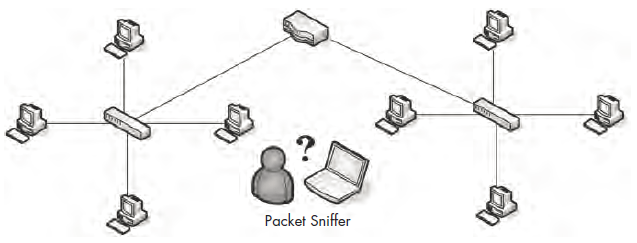
Figure 2-1: Placing your sniffer on the network is sometimes the biggest challenge you will face.
The goal of this chapter is to help you develop an understanding ofpacket-sniffer placement in a variety of different network topologies. Butfirst, let’s look at how we’re actually able to see all the packets that cross thewire we’re tapping into.