I. What is IDS
An IDS (Intrusion Detection System) is a network security device that monitors network transmissions in real-time and issues alerts or takes active response measures when suspicious transmissions are detected. Unlike other network security devices, IDS is an active protection technology. Many medium and large enterprises and government agencies deploy IDS. To use an analogy, if a firewall is the lock on a building’s door, then IDS is the surveillance system inside the building. Once a burglar enters the building or an insider crosses boundaries, only a real-time surveillance system can detect the situation and issue a warning.
Professionally speaking, IDS monitors the network and system status according to certain security strategies to as much as possible detect various attack attempts, attack behaviors, or attack results to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of network system resources. Unlike a firewall, an IDS is an out-of-band monitoring device, which does not require interfacing with any links. It can function without any network traffic passing through it. Therefore, the only deployment requirement for IDS is that it should be connected on all links through which concerned traffic must flow.
IDS Access Method: Parallel Access (Parallel)
The IDS is usually positioned as close as possible to the attack source and the protected resources in a switched network. These positions are typically:
- On the switch in the server area
- On the adjacent switch to the border router
- On the LAN switches of key protected segments
II. The Role and Necessity of Intrusion Detection Systems
Necessity:
- The complexity of network security itself makes passive defense methods powerless
- Concerning firewalls: network boundary device; can be breached; weak protection against certain attacks; not all threats originate from outside the firewall
- Intrusions are easy: intrusion tutorials are widespread; various tools are readily available
Role:
- An important supplement to firewalls
- Important part of building a network security defense system
- Overcome the limitations of traditional defense mechanisms
III. Functions of Intrusion Detection Systems
- Monitor and analyze user and system activities
- Check system configurations and vulnerabilities
- Manage operation system logs and identify user activities that violate security policies
- Make appropriate responses to detected attack behaviors, such as alerts, process interruption, etc.
IV. Classification of Intrusion Detection Systems
By Intrusion Detection Form
- Hardware Intrusion Detection
- Software Intrusion Detection
By Target System Type
- Network Intrusion Detection
- Host Intrusion Detection
- Hybrid
By System Structure
- Centralized
- Distributed
V. Architecture of Intrusion Detection Systems
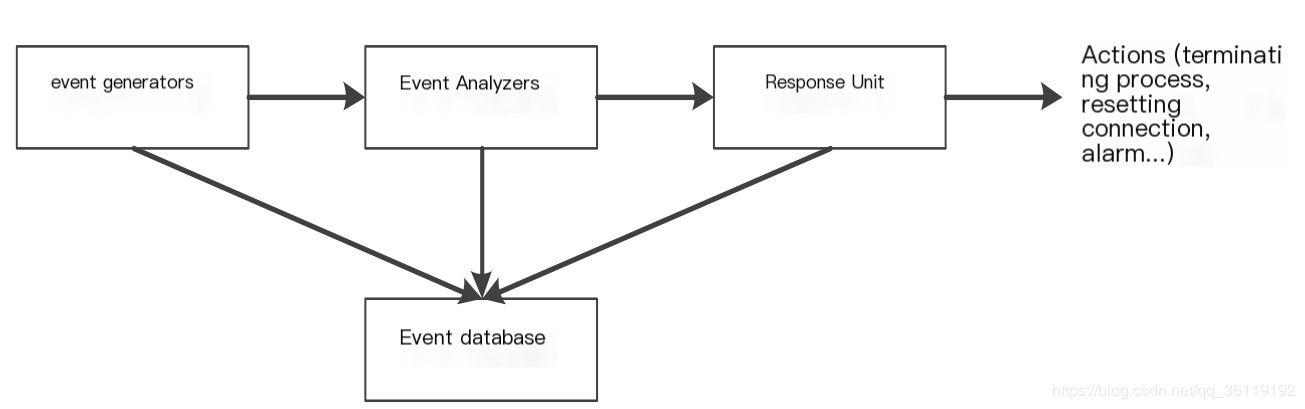
- Event Generator: Its purpose is to obtain events from the entire computing environment and provide them to other parts of the system.
- Event Analyzer: Analyze data, detect dangerous or abnormal events, and notify the response unit
- Response Unit: Reacts to the results of the analysis
- Event Database: Stores various intermediate and final data
 >
>
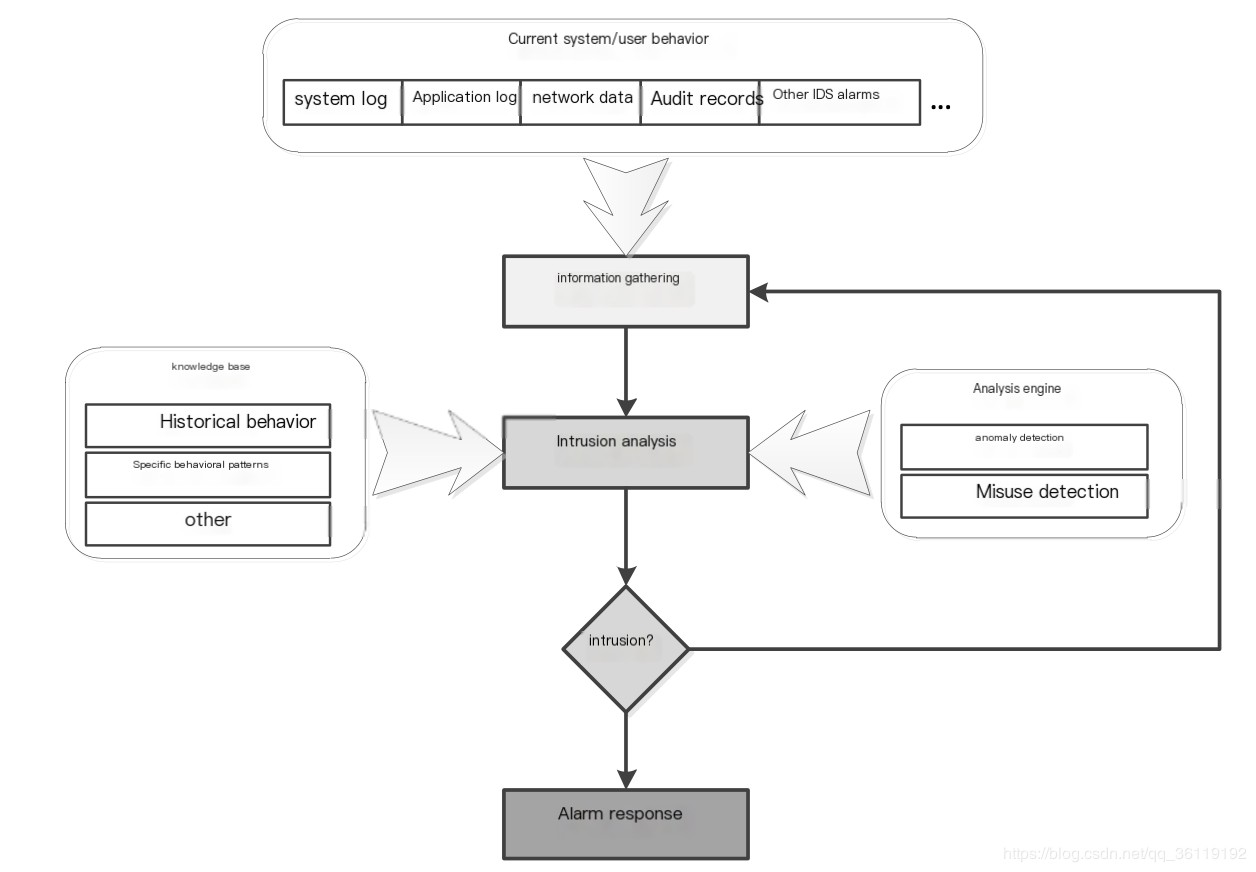
VI. Intrusion Detection Process
 >
>
VII. Key Performance Parameters of Intrusion Detection
- False Positive: A harmless event is detected by the IDS as an attack event.
- False Negative: An attack event is not detected by the IDS or is deemed harmless by analysts.
VIII. Intrusion Detection Technology
1. Misuse Detection TechnologyBased on pattern matching principles. It collects abnormal operation behavior characteristics, establishes a related feature database, and when monitored user or system behavior matches the database records, the system considers such behavior as an intrusion.
Prerequisite: All intrusion behaviors have detectable characteristics.
Indicator: Low false positives, high false negatives.
Attack Feature Database: When the monitored user or system behavior matches the records in the database, the system considers such behavior as an intrusion.
Features: Using pattern matching, misuse patterns can significantly reduce the false positive rate, but the false negative rate increases. Slight changes in attack characteristics can make misuse detection powerless.
- Establishes an intrusion behavior model (attack characteristics)
- Assumes all possible characteristics can be identified and represented
- Misuse based on system and user
Advantages
- High accuracy
- Simple algorithms
Key Issues
- To identify all attack characteristics, a comprehensive feature database must be established
- The feature database needs constant updates
- Cannot detect new intrusions
2. Anomaly Detection TechnologyBased on statistical analysis principles. It first summarizes the characteristics normal operation should have (user profile) and attempts to quantitatively describe them. When user activity significantly deviates from normal behavior, it is considered an intrusion.
Prerequisite: Intrusion is a subset of abnormal activity. Indicator: Low false negative rate, high false positive rate.
User Profile: Usually defined as a set of various behavioral parameters and their thresholds, used to describe the normal behavior range.
Features: The efficiency of the anomaly detection system depends on the completeness of the user profile and the frequency of monitoring; it doesn’t need to define every intrusion behavior, so it can effectively detect unknown intrusions; the system can self-adjust and optimize according to changes in user behavior, but as the detection model becomes gradually precise, anomaly detection will consume more system resources.
- Set “normal” behavior patterns
- Assume all intrusion behavior is abnormal
- Anomaly based on system and user
Advantages
- Can detect unknown attacks
- Adaptive, self-learning capability
Key Issues
- Selection of “normal” behavior characteristics
- Selection of statistical algorithms and statistical points
IX. Intrusion Response Technology
Proactive Response:Intrusion detection systems can block attacks and influence to change the progress of the attack after detecting an intrusion.
Forms:
- User-driven
- Automatically executed by the system itself
Basic Methods:
- Take counter-actions against the intruder (harsh way; mild way; or intermediate way)
- Correct system environment
- Collect additional information
Passive Response: Intrusion detection systems merely report and log the detected issues in a simple manner.
Forms: Provides information to the user, relying on the user to take the next step in response.
Basic Methods:
- Alerts and Notifications
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol), used in conjunction with network management tools.
X. Deployment of IDS
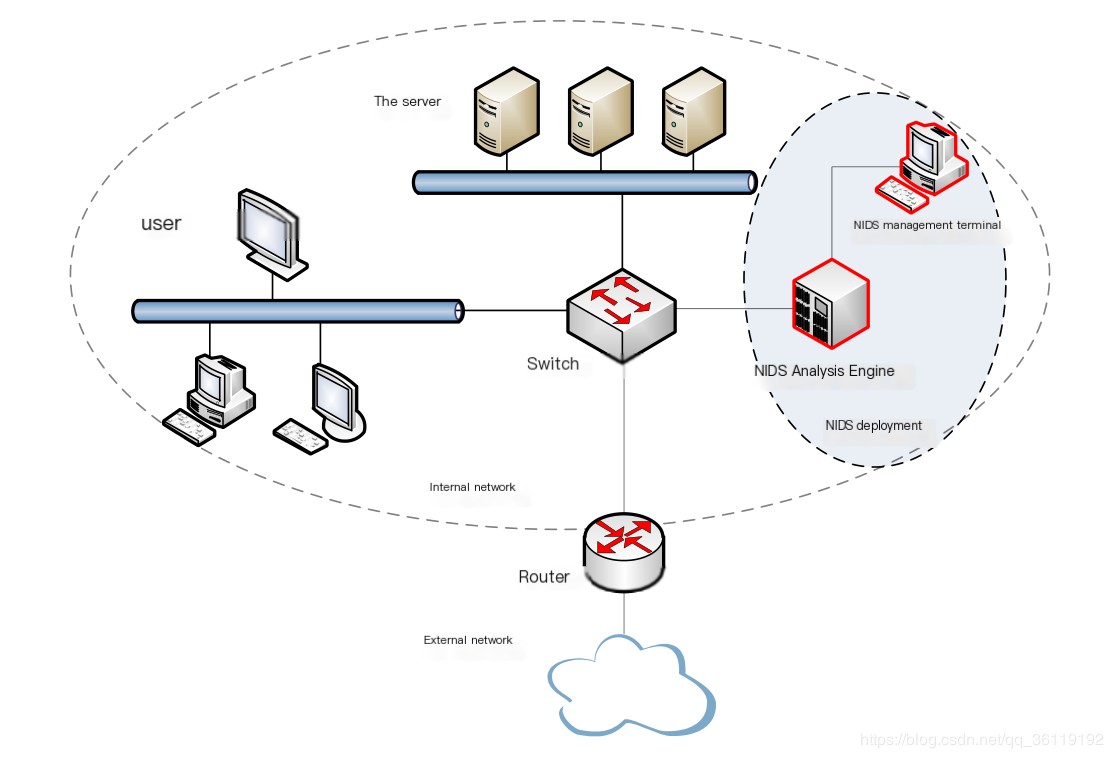
- Network-based IDS
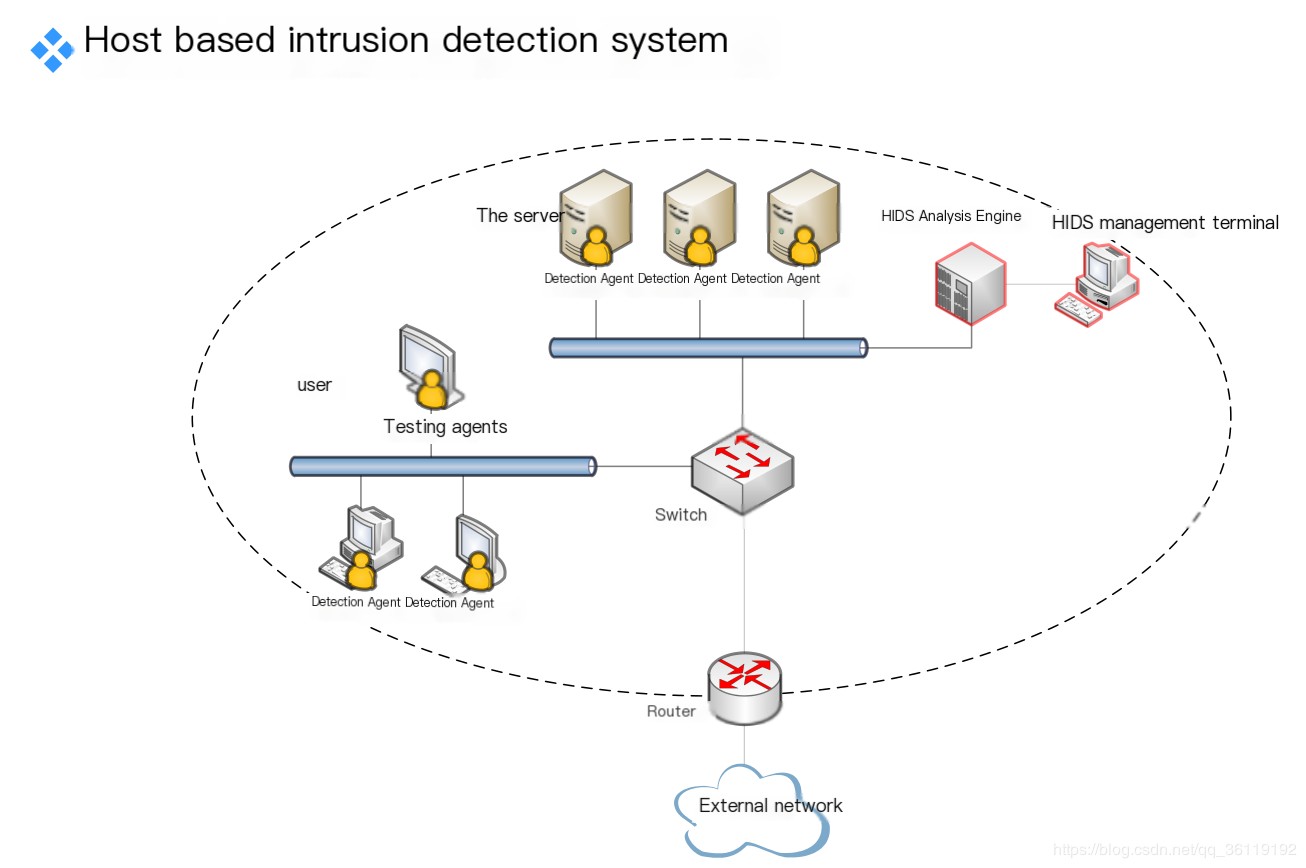
- Host-based IDS
XI. Intrusion Detection Architecture (Features, Advantages, and Disadvantages of Host Intrusion Detection, Network Intrusion Detection, and Distributed Intrusion Detection)
[Differences between HIDS and NIDS: https://blog.51cto.com/mtbaby/1551049]
- Host Intrusion Detection (HIDS)Features: Detects and responds to intrusion behaviors targeting hosts or server systems.Main Advantages::
- Cost-effective
- More detailed
- Low false positive rate
- Suitable for encrypted and exchanged environments
- Insensitive to network traffic
- Determines if the attack was successful
Limitations::
- Depends on host’s inherent logging and monitoring capabilities, host audit information has weaknesses: susceptible to attacks, intruders can escape auditing
- IDS operation more or less affects host performance
- HIDS can only detect actions and logs specific to the host’s users and applications, limiting the types of attacks that can be detected
- Comprehensive deployment of HIDS is costly
- Network Intrusion Detection (NIDS)Features: Uses network cards operating in promiscuous mode to monitor communication traffic on the entire network segment in real-time.Main Advantages::
- Good stealth
- Real-time detection and response
- Difficult for attackers to transfer evidence
- Does not affect business systems
- Can detect unsuccessful attack attempts
Limitations::
- Only detects communication on directly connected segments, cannot detect network packets on different segments
- Has limited detection range in switched Ethernet environments
- It is hard to realize some complex attacks that require extensive calculation and analysis
- Handling encrypted sessions is relatively difficult
- Distributed Intrusion Detection (DIDS)Typically composed of multiple cooperating components, distributed throughout the network, each performing respective functions, such as data collection and data analysis. A central control component performs data aggregation, analysis, and the response to intrusion behaviors.
- Comparison of Network and Host Intrusion Detection: Project HIDS NIDS False Positive Low Certain Amount False Negative Related to technical level Related to data processing capability (unavoidable) System Deployment and Maintenance Regardless of network topology Related to network topology Detection Rules Few Numerous Detection Characteristics Event and signal analysis Feature code analysis Security Policy Basic security policy (point policy) Operational security policy (line policy) Security Limitations All events reaching the host Non-encrypted, non-secure information in transit Security Risks Violation events Methods or means of attack
XII. Limitations of Intrusion Detection Systems
- Requires high user knowledge, configuration, operation, and management are complex
- As the network develops rapidly, the processing performance requirements of intrusion detection systems are increasing, and current technology is difficult to meet practical needs
- High false alarm rate, heavy burden on users for handling
- Due to incomplete warning information records, many warning messages may not be associated with intrusion behaviors, making it difficult to obtain useful results
- When dealing with attacks on itself, detection of other data may also be suppressed or impacted
XIII. Open Source Intrusion Detection Systems
[Table Source: https://www.cnblogs.com/sztom/p/10217345.html]
|
IDS |
HIDS/NIDS |
Unix |
Linux |
Windows |
MacOS |
Remarks | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Snort |
NIDS |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Created by Cisco |
|
2 |
OSSEC |
HIDS |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes | |
|
3 |
Suricata |
NIDS |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Replacement for Snort |
|
4 |
Bro |
NIDS |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes | |
|
5 |
Sagan |
Both |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Replacement for OSSEC |
|
6 |
Security Onion |
Both |
No |
Yes |
No |
No | |
|
7 |
AIDE |
HIDS |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes | |
|
8 |
Open WIPS-NG |
NIDS |
No |
Yes |
No |
No | |
|
9 |
Samhain |
HIDS |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes | |
|
10 |
Fail2Ban |
HIDS |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Copyright Statement: The content of this article is contributed by internet users and only represents the author’s personal views. This site only provides information storage space services and does not own all rights nor assume related legal responsibilities. If this site contains suspected infringement/illegal content, please send an email to report. Once verified, this site will delete it immediately.


