Introduction
The CIA triad is a fundamental concept in information security, representing the three key principles: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability. These principles guide the protection of information and systems, ensuring that sensitive data is accessed only by authorized individuals, remains accurate and trustworthy, and is accessible when needed. Understanding the CIA triad is crucial for implementing effective security measures and mitigating risks.
Without logic, there’s no system; without a system, where’s the efficiency?
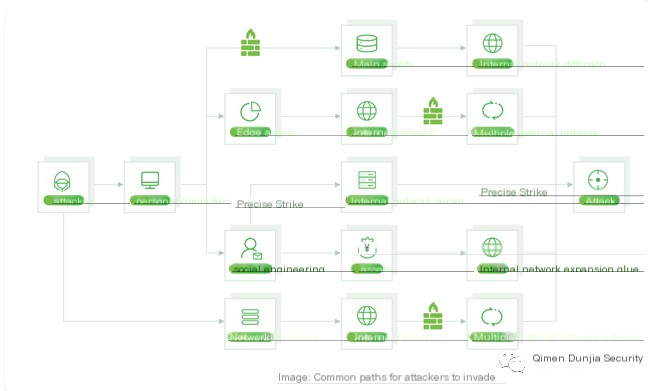
I. What is intrusion?
Intrusive actions refer to the malicious behavior of intruders who, through unreliable intentions (potential, premeditated, unauthorized access), attempt to make a system unreliable or unusable. This is done by bypassing normal identification, authentication, access authorization, audit evasion, and accountability. These abnormal processes or measures damage the information security triad (C confidentiality, I integrity, A availability) of an information system.
 >
>
(This is from the official website of Chaitin Technology. If there is any infringement, please notify the author to remove it.)
The impact of intrusive actions depends on the extent of damage to the CIA triad of information security, business pressures, regulatory pressures, and other factors.
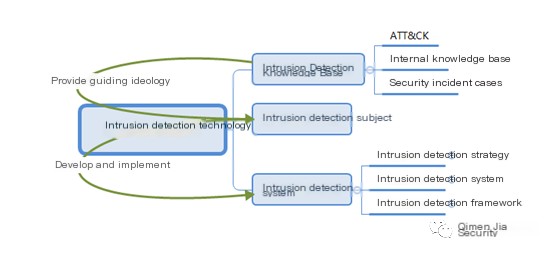
II. What is intrusion detection technology?
Enterprise Intrusion Detection Technology: Intrusion detection technology is a supplement to existing intrusion prevention technologies. It is a means for the bodies implementing intrusion detection to build a detection system and knowledge base, prevent, detect, mitigate intrusions, restore intrusion processes, and respond to events. Essentially, it is a method based on information technology, utilizing a structured system of intrusion detection knowledge, rather than just the narrow technical IT tools as defined by technical personnel.
Structurally, intrusion detection technology includes: detection systems, knowledge bases, and implementing bodies among other sub-structures.
 >
>
Outdated intrusion detection concept:
“Intrusion detection is a reasonable supplement to firewalls, helping systems combat network attacks and extending the security management capabilities of system administrators (including security audits, monitoring, offense identification and response), enhancing the integrity of the information security infrastructure. It collects information from several key points within a computer network system, analyzes it to see if there have been any security policy violations or signs of attack. Intrusion detection is considered the second line of defense after the firewall, monitoring the network without affecting performance to provide real-time protection against internal and external attacks as well as mishandling.”
—- BaiDu Baike’s definition of intrusion detection
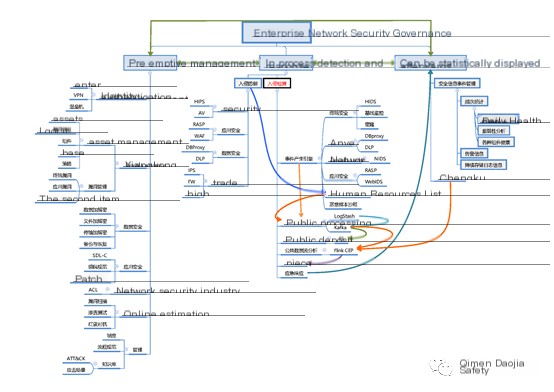
III. In what position does intrusion detection reside in the security operations (management) system?
IV. What issues does intrusion detection technology solve?
1. To fill the gaps in existing intrusion prevention solutions based on access control and fine-grained features through characteristics, models, anomaly detection, and other means.
2. To address monitoring blind spots due to objective factors (such as deployment location or monitoring policies) in intrusion prevention systems. (For example, IPS deployed at boundary positions and the inability to address Windows system component misuse by antivirus.)
3. To mitigate intrusion behaviors in highly available scenarios where intrusion prevention systems are not deployed or defense policies are relaxed, leading to defense bypass. Over-reliance on known intrusion prevention systems without heuristic rules based on anomalies carries risks of being bypassed by variant intrusion methods.
4. In complex intrusion scenarios, to identify suspicious intrusion behaviors that cannot be directly judged by features. (For instance, a single behavior may be normal, but a chain of behaviors combined over time is anomalous.)
5. To detect unknown (those that cannot be judged directly or indirectly based on existing features) and generate anomaly alerts for intrusive behaviors.
V. What is an intrusion detection system?
Intrusion detection system is the protocol and framework established by the implementing body based on the intrusion detection knowledge base to combat intrusive actions. It abstracts from an overly broad, unclear security operations framework and further abstracts the intrusion detection system.
Defines internal corporate intrusion detection policy, detection strategy, framework. The subject of intrusion detection provides design guidelines based on the intrusion detection knowledge base, aiding greatly in event restoration after detecting intrusive behaviors.
VI. What issues does the intrusion detection system resolve or mitigate?
1. It compensates for the shortcomings of existing frameworks that contain commercial solutions not well-adapted (“unaccustomed”) to their environment:
- Difficulty in environmental adaptation: Due to high generality requirements of commercial solutions and limited understanding of internal environments, there is difficulty in matching and adapting to corporate environments.
- Poor scalability: Some commercial solutions fail to meet scaling needs upon business scale increase.
- Poor extensibility: Products are challenging to autonomously control, with limited extensibility, failing to meet other customization needs of the enterprise.
- Poor customizability: Limited perception capability in non-general scenarios, difficult to address security engineers’ need for customized policy based on the internal environment.
- Poor correlation, unable to perfectly integrate with existing intrusion detection frameworks and instances.
2. Compensates for low efficiency in intrusion detection resolution through intrusion detection.
- Functioning independently, loose and chaotic intrusion detection instances fight alone, unable to unite cohesively, not forming a strong perception capability. Each instance generates a flood of alerts, lowering the efficiency of the implementing body’s response. Over time, a “boy who cried wolf” phenomenon could desensitize the implementing body, leading to loss of combat ability.
- Cross-validation and joint analysis among system instances within the intrusion detection framework reduce false alarm rates.
3. Resolves issues of lacking complete standardized procedures
- Establishes systems, strategies, and standardized processes within the intrusion detection framework, enhancing prevention, detection, mitigation, event restoration, and response capabilities at a systemic level, rather than relying on individual skill and experience of detection instances, chaotic and unordered resolution of above issues.
4. Enhances awareness capability (with low collaboration capability) in complex intrusion scenarios:
- Improving collaboration between intrusion detection technologies: with rapid advancement in internet technologies, the spread of 0day, Nday, and advanced threats, counteracting the exploitation of various Web applications, other applications, and operating system 0day, Nday vulnerabilities, if intelligence collaboration (including implementing body proactively obtaining threat intelligence or receiving third-party commercial vendor intelligence pushes) is not efficient; institutionally crafted measures, strategies timely and accurately deployed in a security system, void of collaborative detection, makes efficient collaboration of diverse factors like institutions, strategies, and frameworks impossible;
- Improves collaboration ability between various elements within the framework: The finite merging and efficient collaboration between systems, strategies, frameworks, and implementing bodies in intrusion detection framework helps tackle difficulty in sensing behaviors within complex intrusion scenarios.
- Compensates for deficits in detection capabilities under static, unintegrated resources: Static, non-integrated resources and environments dealing with multi-faceted, diverse intrusion scenarios face challenges from prevention processes, operational efficiencies, and outcomes, making it tough to meet existing intrusion demands. The dynamic, expandable nature of intrusion detection systems is dictated by shifting intrusion risks enterprises face; static systems imply defects, blind spots, and lack of maintenance. The creation of intrusion detection systems precisely aims to solve these issues through efficient intruder behavior detection.
5. Resolves issues of transferring experiential knowledge to the system with reference to the CIA triad.
1) Post-event response through review optimizes the intrusion detection knowledge base, which in turn empowers the system creating a response loop.
6. Addresses issues of excessive system, policy, and framework coupling to achieve decoupling within the intrusion detection system’s institutions, strategies, and framework, emphasizing the CIA triad.
- Ease of synchronization from policy change to strategy, framework becomes challenging;
- Instances of one solution type experiencing issues could lead to functionality failure in other instances;
- Avoid excessive coupling between implementing body and framework, where a personnel departure causes inadequate maintenance and affects the normal operation of the intrusion detection system;
- Avoid excessive coupling between instances where faults in one lead to wide-reaching impact across the system;
- Besides complex intrusion scenarios, frameworks should detect most intrusion behaviors, avoiding changes in bodies affecting framework perception, event restoration, etc. During framework instance development, efforts should be made to use user-friendly, maintainable components that meet assessment requirements.
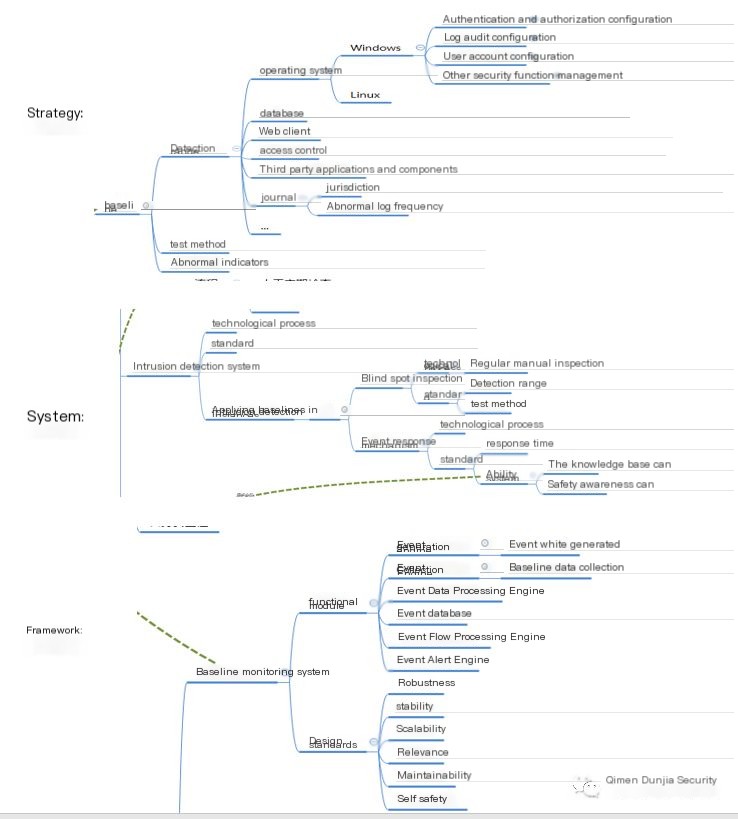
VII. What is an intrusion detection framework?
Intrusion detection framework defines system creation from the intrusion detection implementation’s perspective with system, strategy, intrusion detection framework design requirements, providing design standards (such as stability, robustness, maintainability, expansion, relevance, own security), guiding thoughts on feature modules (event generation engine, event collection engine, event data processing engine, event database, event flow processing engine, event alert engine). It serves to enhance synchronization, integration, and decoupling.
Brilliant
VIII. What is an intrusion detection system?
Intrusion detection system is a structured system instance set designed according to intrusion detection framework requirements, providing automated monitoring, auditing, mitigation, blocking, and event restoration functionalities for intrusion behaviors. Each system instance contains four basic modules: event generation, event database, event analysis engine, and event alert engine trigger. Depending on the enterprise environment, the database, analysis engine, and alert engine across instances may be unified to varying degrees. Modules might intersect or combine in an unpredetermined sequence forming a holistic entity.
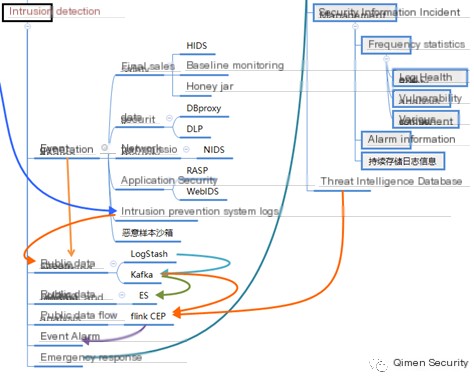
IX. What system instances should an intrusion detection system include?
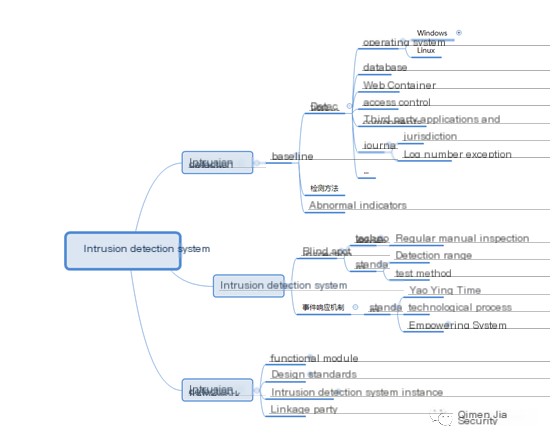
1. Baseline monitoring system: A near-real-time or scheduled baseline monitoring system for baseline security policy collection, auditing, configuration. A baseline system may also integrate into HIDS, or rely on advanced auditing features inherent to operating systems as an engine.
Q: Why is a baseline monitoring system part of an intrusion detection system?
A: Because, during intrusion, prevention, and mitigation strategies may alter attacker TTP, causing changes in baseline policy within the CIA triad.
2. Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS): A system based on network traffic characteristics, models, and heuristic logic for monitoring, auditing, control (traditional NIDS and model-based Web IDS/WAF);
Q: Why are NIDS needed when firewalls and WAFs exist?
A: The reasons can be derived from the issues that intrusion detection technology addresses in relation to the CIA triad.
3. Host-based Intrusion Detection System (HIDS): A system monitoring against operating system programs, executable codes, suspicious operations based on terminal behaviors;
4. Antivirus System (AV): Terminal-based systems offering monitoring and control against malicious programs, malicious code executions in intrusion defenses against threats like Trojans, viruses, worms, ransomware;
Q: Why is an antivirus system part of an intrusion detection system?
A: Malicious features may be defined before intrusion, and logs may appear in antivirus system instances during malicious behaviors, offering exception signals to the framework.)
5. Data Leakage Prevention System: Systems based on terminal or network for preventing, detecting, mitigating the non-standard process or event of transferring, stealing, copying confidential information (HDLP, NDLP, behavior audit), non-trusted device monitoring systems;
Q: Why is a data leakage prevention system part of an intrusion detection system?
A: It not only prevents internal entities from copying, transferring corporate confidentiality but also prevents external entities. When intrusion events occur, linkage to data leakage prevention system aids in event restoration, attribution for external intrusion actions failing to preserve confidential data.
6. Public flow data processing engine: Omitted
7. Public security information event management system: A system based on event processing procedures providing event alerts, display management.
8. Threat intelligence system: Implementing bodies proactively obtain threat intelligence through various channels or acquire products of threat intelligence vendors;
9. Malware sample analysis sandbox: A hybrid method-based sandbox for detecting malicious files by analyzing characteristics and behaviors of unknown files.
10. Honeypot Decoy System: Information systems based on fake/real status integration traps and decoys for intrusion intelligence collection (honeypot);
11. Other expandable systems monitoring, auditing, controlling abnormal measures or processes;
X. Intrusion detection framework detection process
1. Direct anomaly detection based on single-instance single-point sensing
2. Sequence anomaly detection based on single-instance multi-point sensing
3. Composite event detection based on exceptions across multiple instances within a short timeframe
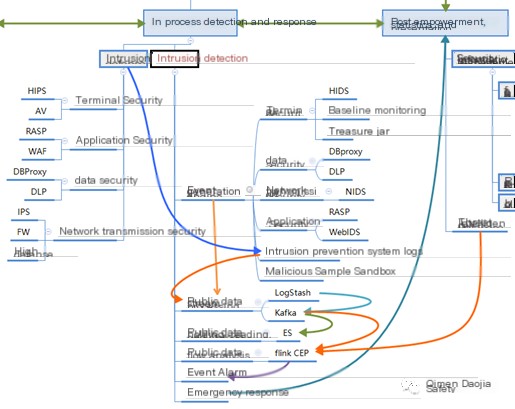
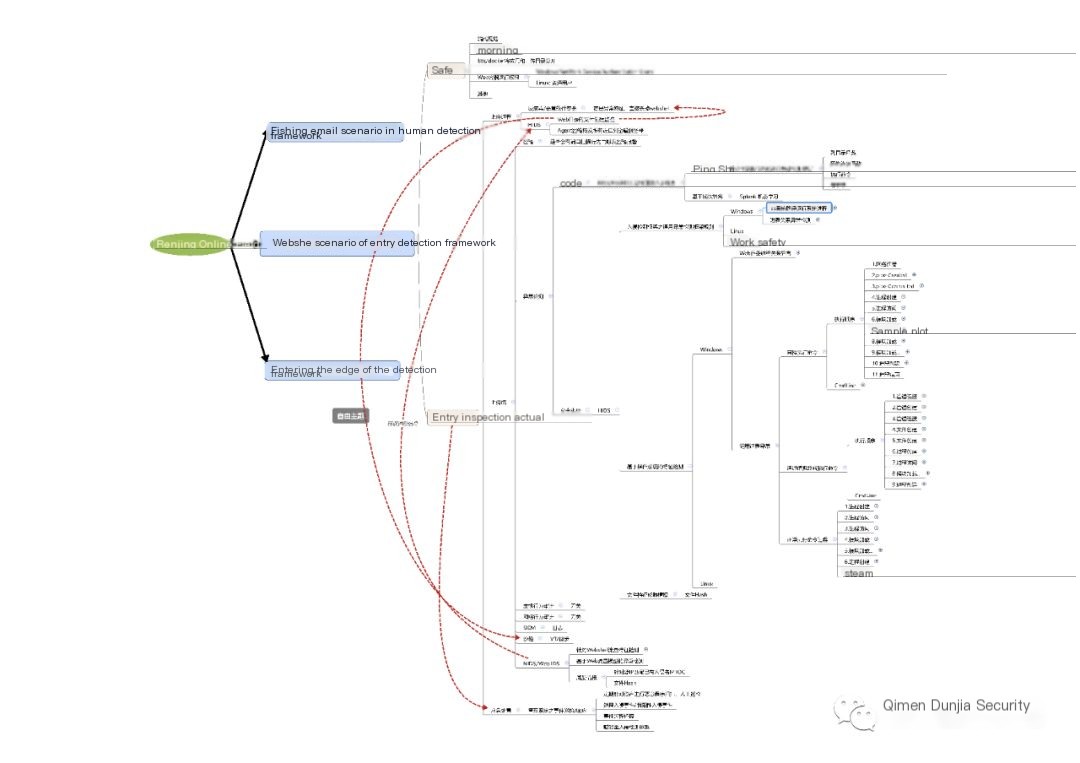
XI. Simple application of intrusion detection framework based on Webshell scenario