Security researchers have recently identified numerous reflection DDoS attacks that exploit vulnerabilities in the Joomla Google Maps plugin. This highlights a new risk involving “Joomla Reflection DDoS.”
Researchers from Akamai Technologies’ Prolexic Security Engineering & Response Team (PLXsert) identified a vulnerability within the Google Maps plugin that enables attackers to turn Joomla servers, where the plugin is installed, into tools for conducting DDoS attacks. Alarmingly, this method, known as “Joomla Reflection DDoS,” is very low-cost and easy to execute.
Joomla Reflection DDoS
Reflection DDoS appears to be the new trend among DDoS attackers. In the fourth quarter of 2014, Akamai observed that 39% of DDoS attack traffic utilized reflection methods, which exploit network protocols or software vulnerabilities to reflect malicious traffic onto third-party servers or devices. Distributed reflection denial-of-service attacks are very common among underground criminals.
Hackers exploited a vulnerability in a Joomla (a well-known content management system abroad) Google Maps plugin discovered in early 2014.
“In February 2014, multiple vulnerabilities were discovered in Joomla’s Google Maps plugin, one of which allowed the plugin to act as a proxy. Vulnerable servers were collectively used for reflection attacks initiated by tools like DAVOSET and UFONet.”
The report states:
Using DAVOSET to launch Joomla reflection DDoS attacks is very effective. The software includes a list of servers with exploitable vulnerabilities in the Google Maps plugin. DAVOSET also allows users to employ their own reflection servers, and the program is easy to configure: the number of requests per reflection server, proxy server configurations, etc. UFONet is another tool that can be used for reflection attacks and is also straightforward for conducting Joomla reflection DDoS.
“Like DAVOSET, it utilizes a web interface and point-and-click configuration. These user-friendly features make it effortless for attackers to configure proxies (e.g., Tor), customize headers, and other attack options. Figure 2 shows how attacks are carried out with proxies, while Figure 3 illustrates the tool’s interface.”
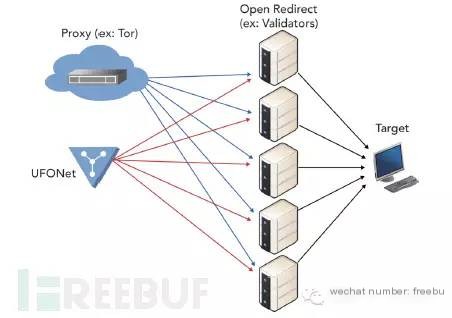
Figure 2
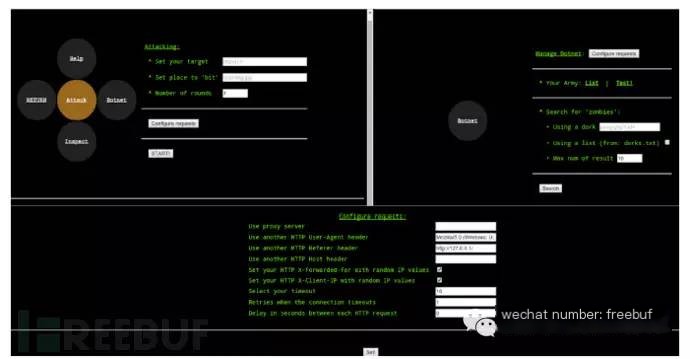
Figure 3
Akamai researchers found that a large number of Joomla sites have been abused by hackers since September 2014, turning them into bots. Nearly 150,000 vulnerable sites are being used for Joomla reflection attacks:
“The signatures in the attack traffic matched those found on websites offering DDoS-for-hire services. Criminals appear to leverage tools specifically designed to exploit XML and Open Redirect functionality, resulting in reflection responses that can be directed at target machines to cause denial of service. These tools are rapidly gaining popularity and being adapted and enhanced for the ‘DDoS-for-hire’ market.”

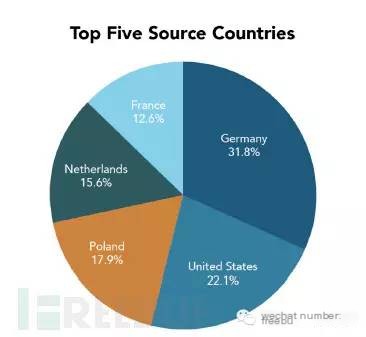
Source of Attacks
Akamai confirmed that these attacks continued into 2015, with the primary sources of attack traffic being Germany (31.8%), the United States (22.1%), and Poland (17.9%).
Defending Against Cloud-Based DDoS Attacks
The report also includes Snort rules for defending against Joomla reflection DDoS attacks. Experts further recommend devising a DDoS defense plan as such attacks are becoming increasingly frequent.
Stuart Scholly, Senior Vice President and General Manager of Security Business Unit at Akamai, stated:
“Vulnerabilities in web applications provided by SaaS (Software-as-a-Service) vendors give cybercriminal groups a foothold. Numerous vulnerabilities form a vast ocean, of which this flaw is yet another web application vulnerability, making it exceedingly difficult to locate. Enterprises need to develop a DDoS defense strategy to withstand the immense traffic resulting from countless cloud-based SaaS servers being used in denial-of-service attacks.”


