In 1998, Martin Roesch developed the open-source intrusion detection system Snort using the C programming language. Today, Snort has evolved into a powerful network intrusion detection/prevention system with features such as multi-platform, real-time traffic analysis, and network IP packet logging, making it one of the top open-source intrusion detection systems in the world. The Snort IDS uses a series of rules to define malicious network activity, matches packets against them, and alerts the user.
Main Uses of Snort:
1. Similar to TCP dump, used as a network sniffer for debugging network traffic.
2. Network intrusion detection for signature recognition.
Example of Using Snort Intrusion Detection System:
1. Capture packets by combining three Snort modes
Win7 access Kali through the following method: 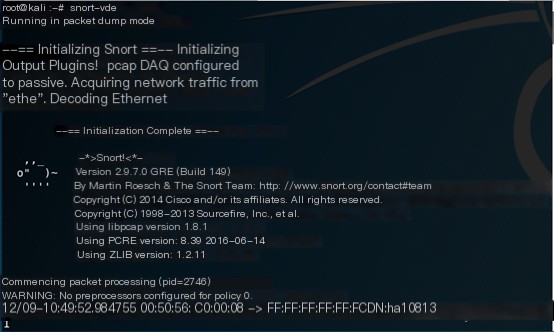
2. Log packets to a specified location
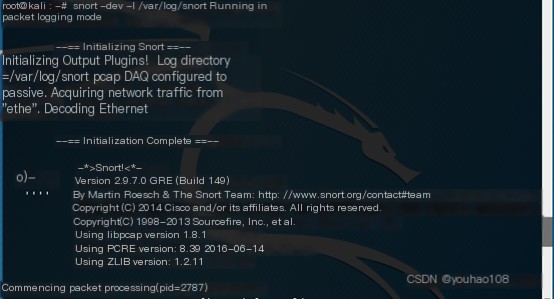
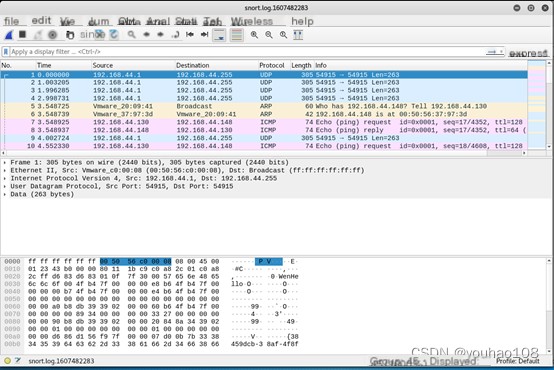
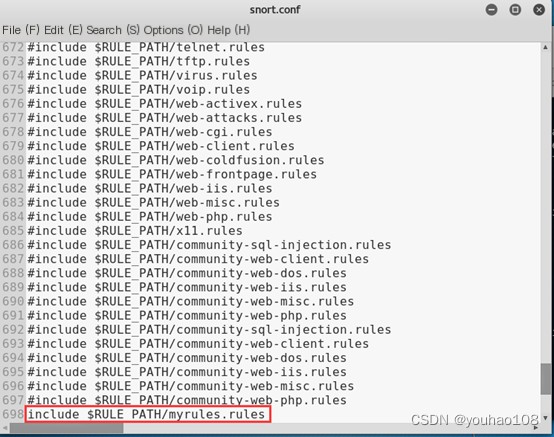
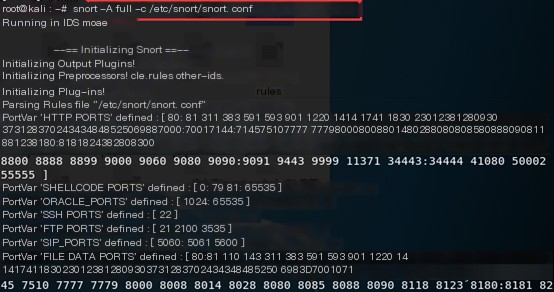
3. Edit Snort configuration files to add custom rules

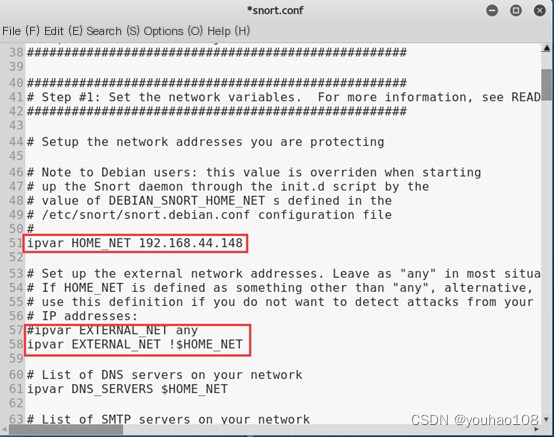


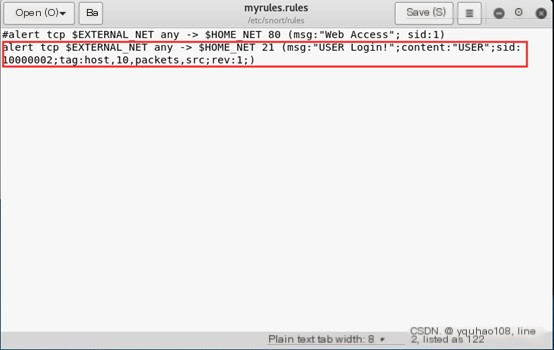
(1) Alert on request packets from external hosts targeting the current host’s 80/TCP port.
Add the following rule: 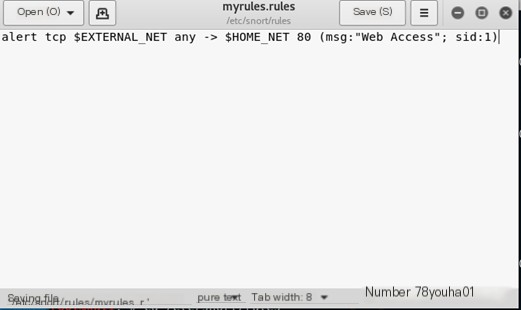
Win7 accessing the Kali server website 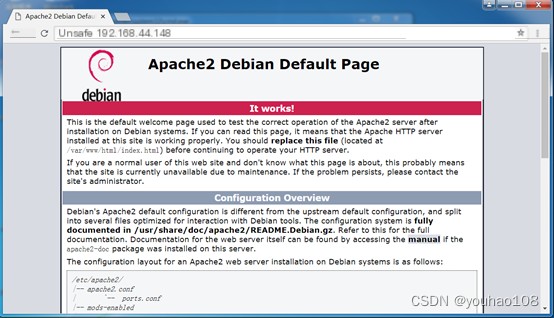
Detect web access 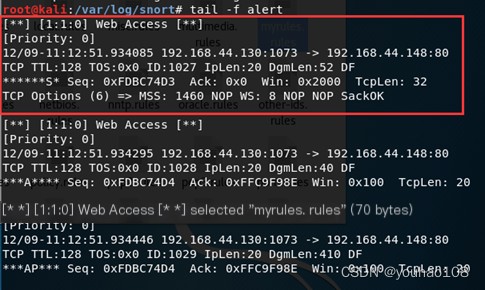
(2) String matching: Alert and capture the username and password if a machine logs into the Kali local FTP server.
 FTP connecting to Kali on Win7
FTP connecting to Kali on Win7 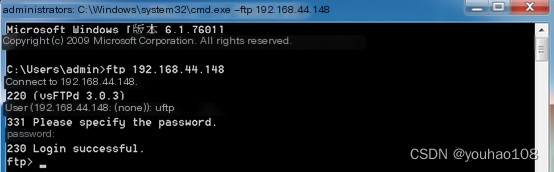 Detect FTP access, inspect the packets to find plaintext username and password
Detect FTP access, inspect the packets to find plaintext username and password 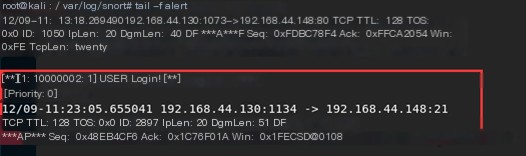
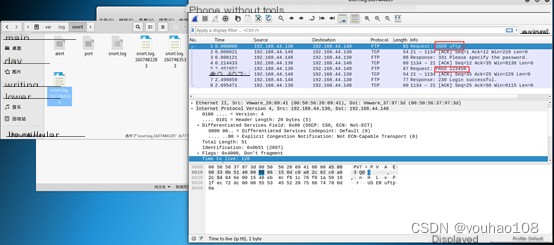
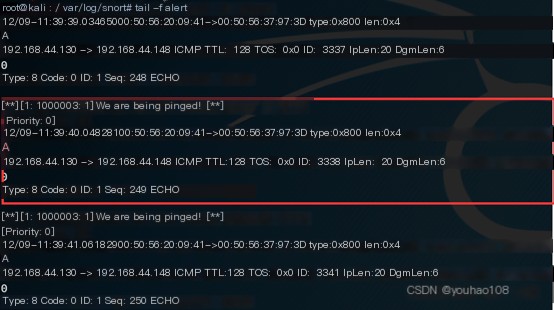
(3) Alert on ICMP echo request Add the following rule: 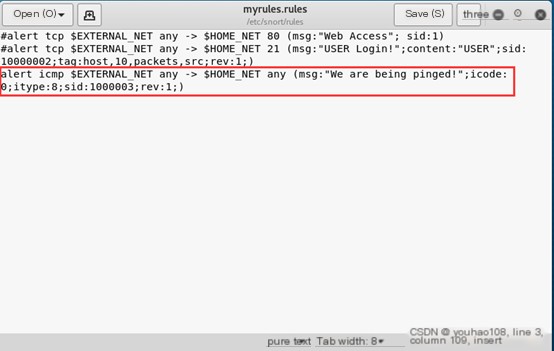
Win7 ping Kali  Detect ICMP response
Detect ICMP response