Introduction to IP Address Conflicts and Network Troubleshooting
In the modern enterprise environment, Local Area Network (LAN) is one of the key infrastructures supporting daily business operations. However, with the continuous expansion of network scale and the continuous advancement of technology, LANs are facing more and more technical challenges.Among them, IP address conflicts and network performance degradation are among the most common problems, which not only lead to network service interruptions but also affect work efficiency.
And we all know that in order to improve security management and informationization, many companies have built very complete office information systems and deployed video surveillance.
However, due to the lack of overall planning or inadequate consideration when selecting network products, network construction often fails to achieve the expected results, and many application problems arise later.
Today, let’s talk about these common problems and see if you are among them.
Today’s article reading bonus: “IP address management open source system-PHPIPAM”
Understanding the importance and complexity of IP address management is essential. Traditional Excel spreadsheets, while sometimes helpful, often fall short in efficiency and accuracy when handling large data volumes and complex network structures.
As the saying goes, there is always a way out. The emergence of PHPIPAM provides us with such a solution.
Who still uses Excel when you have this open source IP address management system? (Click on the blue words to learn how to use it)
Send the code ” PHPIPAM ” in a private message to get this high-quality resource.
Slow Network Cloning Caused by IP Address Conflicts
In a local area network, network cloning usually refers to the process of quickly copying the operating system and applications on one computer to multiple computers . This process is very important for mass deployment of new devices or updating existing devices.
However, in actual operation, slow network cloning speed is a common problem, which directly affects work efficiency and utilization of network resources.
01 Cause Analysis
- Hardware limitations: Slow network interface cards (NICs) or older network equipment can limit data transfer rates.
- Network bottleneck: There may be certain links in the network that become bottlenecks for data transmission, such as insufficient port speed of the switch or limited processing power of the router.
- Improper network configuration: Incorrect network configuration, such as inappropriate subnet division or unreasonable network traffic management strategy, can also lead to a decrease in network cloning speed.
02 Solution
- Upgrade hardware: Replace high-speed network interface cards (NICs) and use switches and routers that support 1G or 10G transmission rates.
- Optimize network configuration: Plan subnets reasonably to avoid unnecessary network segmentation; adjust network traffic management strategies to ensure bandwidth priority during the cloning process.
- Adopt efficient cloning technology: Use PXE (Preboot Execution Environment) boot technology for network cloning to reduce dependence on local storage; use differential cloning technology to speed up the cloning process.
Switch Loops Leading to IP Address Conflicts and Network Disruption
In a local area network, switches connect various devices. However, if the network topology is misconfigured, loops may form, causing serious network problems and potentially paralyzing the entire network.
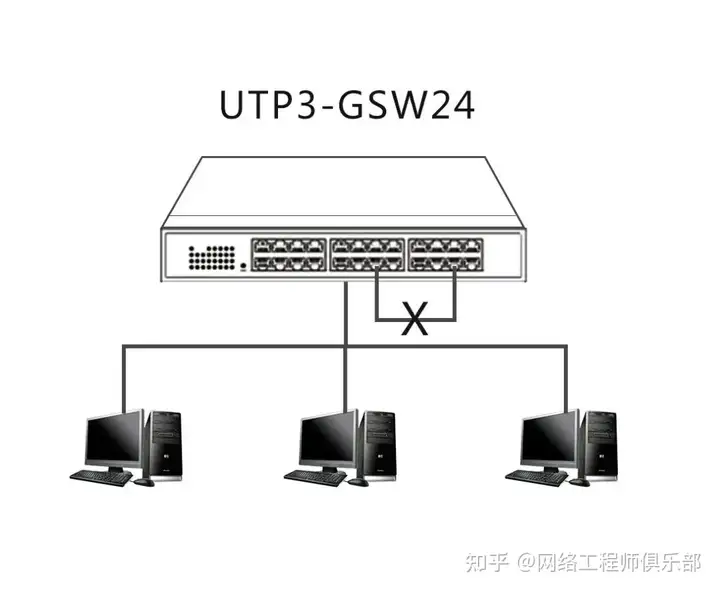
01 Cause
- Improper network cabling: Incorrect physical connections, such as two cables connected to the same set of ports.
- Redundant connections: The redundant paths set up to increase network availability are not configured correctly.
- Misconfiguration: Improper switch port configuration, such as enabling unnecessary ports or incorrect VLAN settings.
02 Solution
- Enable STP ( Spanning Tree Protocol ): You can prevent loops from forming by enabling the Spanning Tree Protocol, which automatically shuts down redundant links in a loop.
- Network topology optimization: Re-evaluate the network topology design, remove unnecessary redundant connections, and simplify the network structure.
- Avoid unnecessary redundant connections: Establish redundant paths only when necessary and ensure that these paths do not form loops.
Resolving IP Address Conflicts Due to Small Routers and Mismanagement
In a local area network, IP address conflicts are usually caused by two or more devices being assigned the same IP address. This may cause network connections to be unstable or some devices to be unable to access the network.
01 Cause
- Manual configuration error: The administrator made an error when manually configuring IP addresses and assigned the same address to multiple devices.
- DHCP server failure: A problem with the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) server, such as a configuration error or software failure, can result in duplicate IP addresses being assigned.
- Small router limitations: Small routers may not have advanced features, such as more sophisticated address management or conflict detection mechanisms , which can easily lead to conflicts.
02 Solution
- Check and repair DHCP configuration: Ensure that the DHCP server is configured correctly, troubleshoot, and plan the address pool range appropriately.
- Use static IP addresses : For critical devices, consider manually assigning static IP addresses to avoid conflicts.
- Increase router functionality: Upgrade to a router with more powerful address management and conflict detection capabilities.
Mitigating ARP Attacks and IP Address Conflicts
ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) virus attack is a common network attack method, which changes the mapping relationship between IP addresses and MAC addresses in the local area network by forging ARP responses, thereby achieving the purpose of man-in-the-middle attack. This attack can cause data leakage, service interruption and other problems.
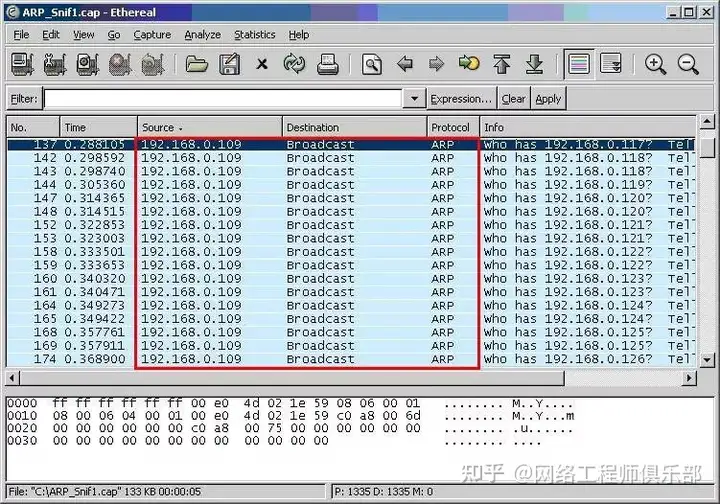
01 Attack Principle
- ARP cache poisoning: The attacker sends a forged ARP response to the target network , binding his own MAC address to the target IP address, so that other devices in the network send data packets to the attacker instead of the real target device.
- Man-in-the-middle attacks :Once an attacker successfully inserts himself into the communication path between the source and destination devices, he can listen in, tamper with, or prevent the transmission of data packets.
02 Solution
- Install antivirus software: Use reliable antivirus software to detect and remove ARP viruses.
- Update security policies regularly: Ensure that the firmware and operating systems of network devices are up to date and follow security best practices.
- Use static ARP table: Manually create static ARP entries to bind the IP addresses of critical devices to their MAC addresses to prevent ARP cache poisoning.
- Enable ARP protection features: Many modern switches and routers support ARP protection features such as ARP Inspection or DAI (Dynamic ARP Inspection), which can verify the validity of ARP responses.
Handling Surveillance Data and Its Effect on IP Address Conflicts
In modern office environments, network monitoring is a necessary measure to ensure network security and compliance. However, excessive monitoring data collection may occupy a large amount of network bandwidth, thus affecting the performance of normal business applications.
01 The impact of data monitoring
- Network bandwidth usage: Continuous data monitoring will generate a large amount of monitoring data streams, which need to be transmitted through the network to the monitoring center or log server .
- Computing resource consumption: Collecting and processing monitoring data requires additional computing resources, such as CPU and memory, which may affect the execution of other tasks on the server.
02 Solution
- Adjust monitoring strategies: optimize monitoring frequency and data collection scope, monitor only necessary information, and reduce unnecessary data traffic.
- Increase bandwidth resources: If monitoring data does occupy a large amount of bandwidth, consider increasing the network bandwidth to ensure that there are enough resources for other services.
- Use a dedicated monitoring network: Consider setting up an independent network channel for monitoring data to avoid competing for bandwidth with business traffic.
- Optimize data processing: Use more efficient algorithms and technologies to process monitoring data and reduce the consumption of server resources.