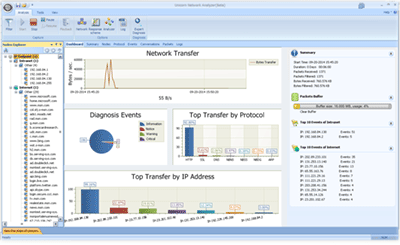
Overview: This article provides a detailed introduction to the Colasoft Network Analysis System-CSNAs-Tech . .*. version 32, a professional-grade network monitoring and analysis tool designed for 64-bit operating systems. With powerful real-time data capture and analysis capabilities, the system helps users gain deep insights into network traffic behavior, troubleshoot issues, and ensure network security. The article delves into core functionalities such as real-time network monitoring, traffic analysis, event triggering and alerts, security analysis, and application identification and performance optimization. It also explores use case scenarios like network failure diagnosis, network security auditing, performance tuning, and regulatory compliance checks. Finally, the article outlines installation and usage steps, along with the necessary hardware and software environment requirements. 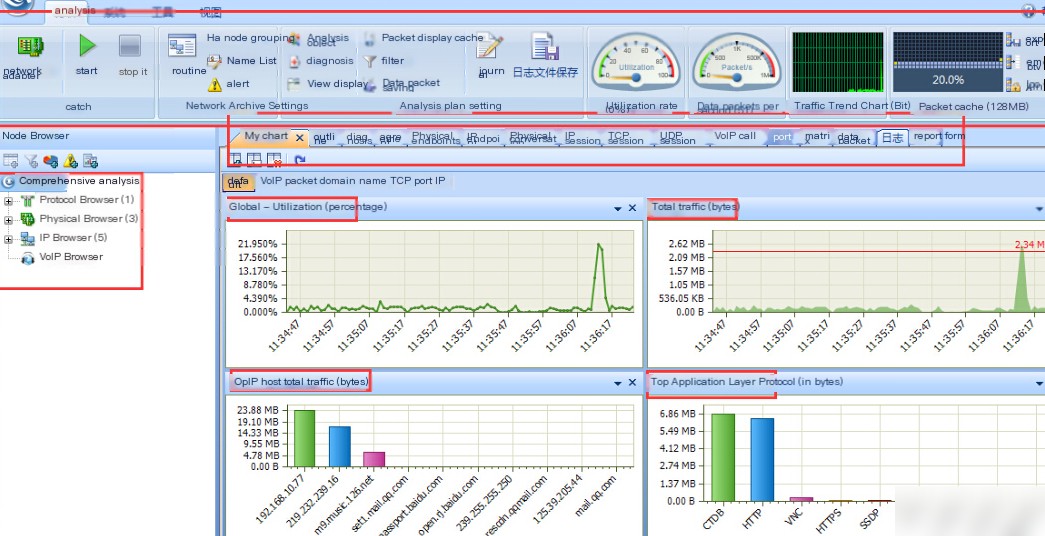
Colasoft Network Analysis System: Overview and Versions
In today’s digital era, IT systems have become an indispensable part of enterprise operations. This chapter provides an overall understanding of the system, including its features, architecture, and differences between various versions. It also discusses the design philosophy of the system and guidance on selecting the appropriate system version based on the needs of different organizations.
System Overview: Colasoft Network Analysis System
First, the system is an integrated platform comprising various software components aimed at meeting specific business requirements. It generally includes components such as data storage, data processing, and application logic. The system’s design considers ease of user interface, data security, and scalability. By leveraging architectural design, the system ensures that all components work cohesively to deliver efficient services.
Version Differences in Colasoft Network Analysis System
Different system versions typically come with varying features and performance improvements. New versions may introduce additional functionalities, fix vulnerabilities in previous versions, or optimize existing features. Users should evaluate their business needs and technical requirements when choosing a version. For example, startups may favor versions with rapid deployment capabilities, while established organizations might prioritize advanced features and customization options.
Design Philosophy of Colasoft Network Analysis System
The system’s design philosophy revolves around addressing specific problems or meeting defined requirements. This could include improving efficiency, simplifying processes, automating repetitive tasks, or providing advanced data insights. Understanding the system’s design goals can help users better leverage it to achieve business objectives.
In the next chapter, we will dive into real-time network monitoring features, a critical component in ensuring IT system stability.
2. Real-Time Network Monitoring Features
2.1 Fundamental Concepts of Network Monitoring
2.1.1 Purpose and Importance of Monitoring
The purpose of network monitoring is to ensure the stability, security, and efficiency of network systems. In modern IT environments, networks are considered the backbone of enterprises, carrying critical business processes and data transmission. Monitoring enables the real-time detection of network status, prevention of network failures, and quick response and recovery in the event of anomalies.
The importance of monitoring is reflected in the following areas:
- Performance Management: Monitoring helps IT administrators understand network performance by tracking and analyzing key metrics such as network latency and bandwidth usage.
- Security Management: By monitoring unusual traffic and security incidents, potential threats such as DDoS attacks and virus outbreaks can be identified promptly.
- Troubleshooting: Detailed information provided by monitoring tools facilitates the rapid identification of issue sources, minimizing downtime.
- Reporting and Compliance: Monitoring reports can be used for internal audits and external compliance requirements, demonstrating that the organization has implemented proper network management and security measures.
2.1.2 Evolution of Monitoring Technologies
The history of network monitoring technology traces back to simple early tools like ping tests and SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol). Over time, monitoring technologies have evolved to include advanced features like traffic analysis, real-time alerts, and data visualization.
- Active Monitoring: Early tools relied mainly on active queries to check the status of network devices and services at scheduled intervals.
- Passive Monitoring: With growing network traffic, passive monitoring emerged, which analyzes network packets passing through monitoring points without sending additional queries.
- Integrated Analysis Tools: Modern monitoring systems integrate various technologies, such as AI-based predictive analytics, to provide warnings before issues occur.
2.2 Technical Implementation of Real-Time Monitoring
2.2.1 Data Capture Mechanisms
Real-time network monitoring systems must efficiently and accurately capture network data. This relies on network probes, proxies, or switch port mirroring to capture packets.
- Network Probes: Connect directly to critical network points to capture all passing packets.
- Proxy Servers: Monitor and record traffic passing through them.
- Switch Port Mirroring: Configures one port of a switch to mirror the traffic of other ports and sends it to the monitoring system.
2.2.2 Real-Time Data Processing Workflow
After data is captured, the monitoring system processes it to extract valuable insights. The workflow generally involves the following stages:
- Data Aggregation: Group and summarize captured packets based on specific rules.
- Traffic Analysis: Analyze aggregated data for patterns and anomalies.
- Alert Generation: Produce alerts based on predefined thresholds and rules.
- Data Visualization: Present processed data to users in charts, dashboards, and other formats.
2.2.3 Monitoring Interface Design and Interaction
An intuitive and comprehensive user interface is crucial for real-time network monitoring. Key design considerations include:
- Interface Layout: Ensure functional areas are well-organized for easy access to primary monitoring functions.
- Real-Time Updates: The interface should refresh in real time to display the latest data.
- User Customization: Enable users to tailor views and alerts to their specific needs.
- Interactivity: Support interactive features such as zooming, dragging, and click-based event responses in charts and dashboards.