1. Preparation for Muyun HIDS
1.1 Deploy Muyun HIDS Security Devices
Deploy host security product: Muyun HIDS
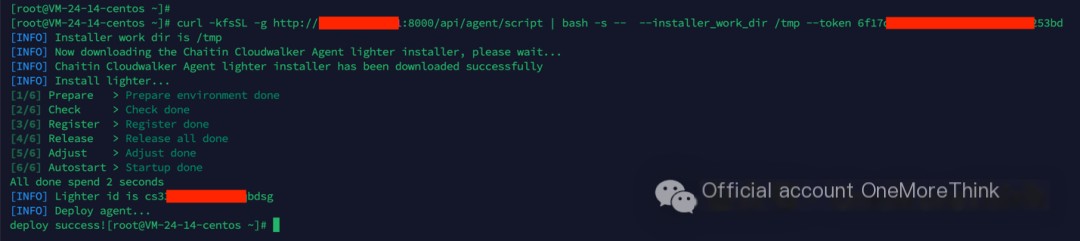 />
/>
2. Detection Using Muyun HIDS
2.1 Muyun HIDS Security Device Alerts
On October 20, 2024, at 8:53:31 PM, Muyun HIDS detected malicious files on the server: /etc/pm/ /z
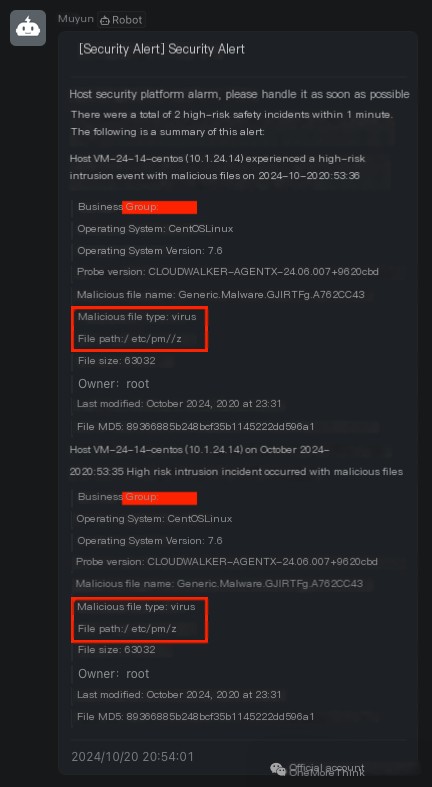 />
/>
Logging into Muyun HIDS, a total of 4 malicious files were found:
1、/etc/pm/’ ‘/z
2、/etc/xdg/’ ‘/.cm/mig
3、/etc/udev/’ ‘/.c/init
4、/etc/X11/.lans/scan2
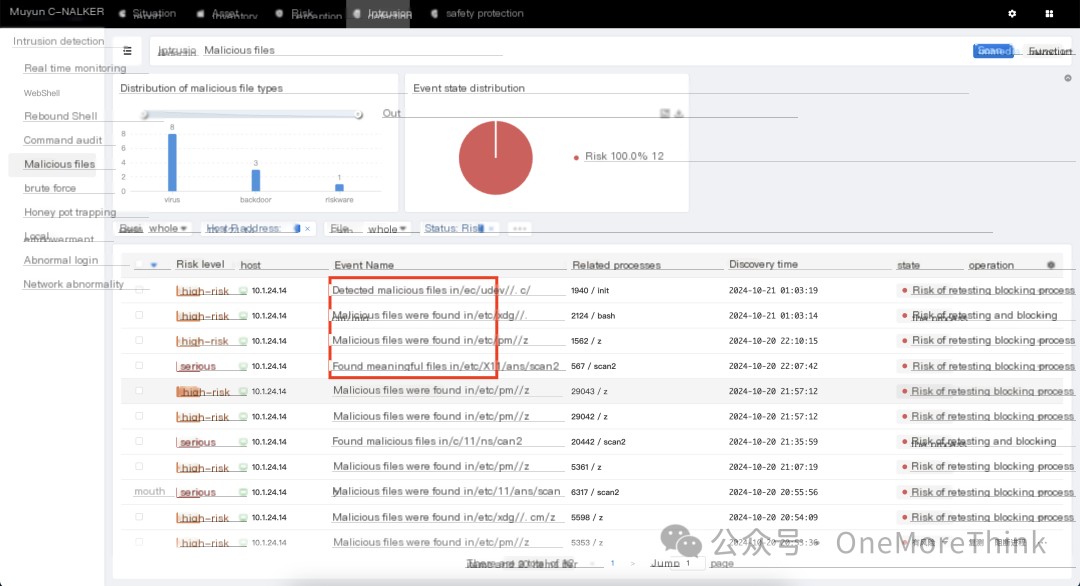
No other alerts were found.
3. Containment with Muyun HIDS
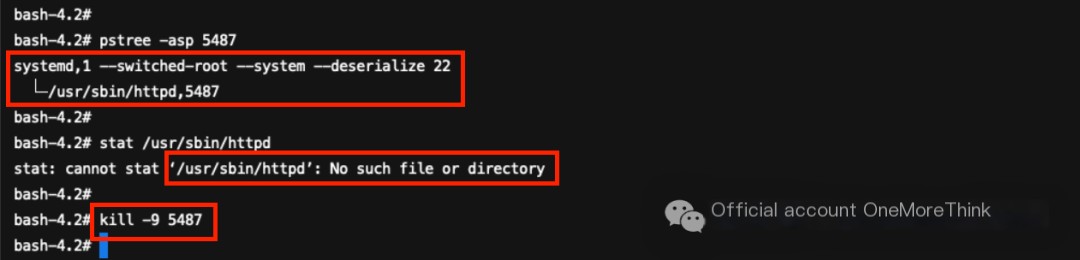
3.1 Terminate Processes Related to the Malicious Program /usr/sbin/httpd Using Muyun HIDS
The /usr/sbin/httpd process 5487 maxed out the CPU.
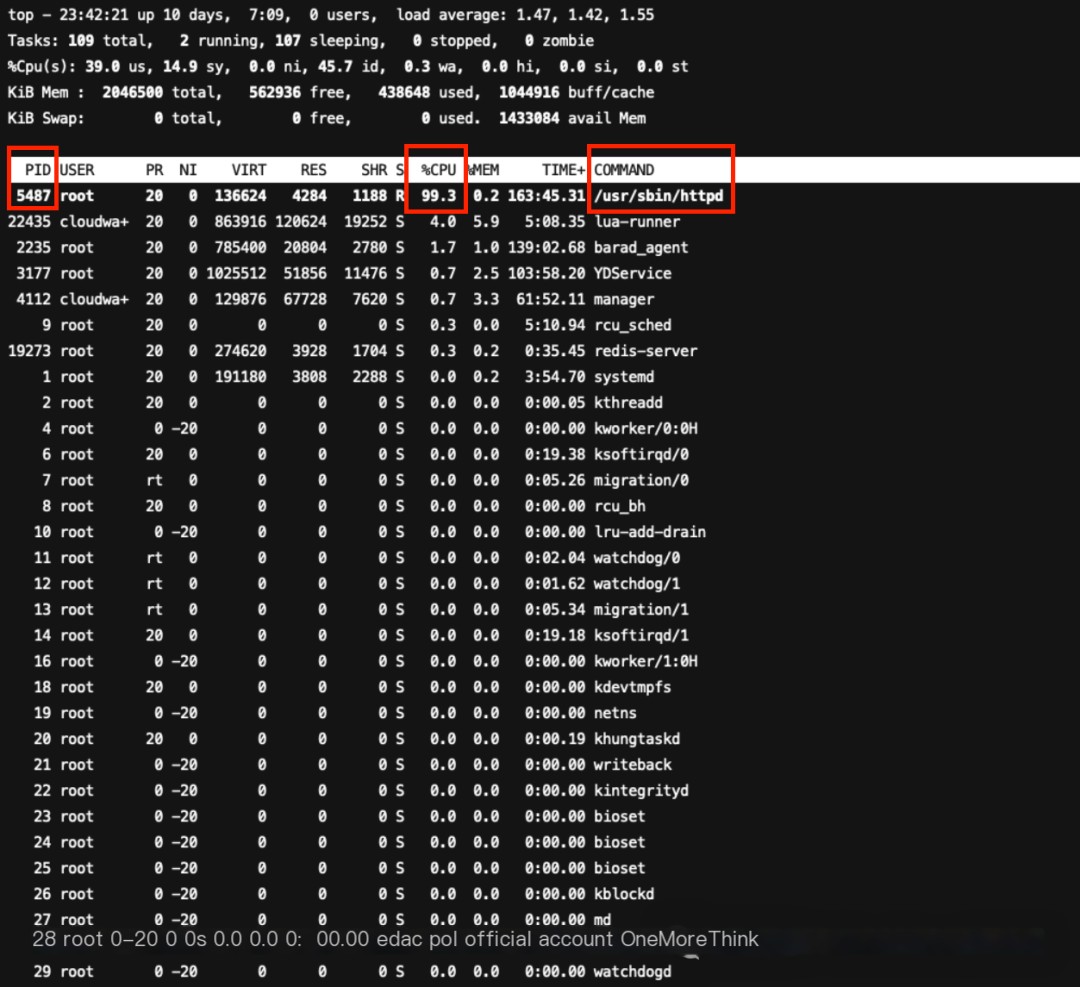
This process has no parent process and can be killed directly.
The program could not be found; nothing to delete.
3.2 Muyun HIDS Termination of Network-Based Malware: `/etc/pm/’ ‘/z`
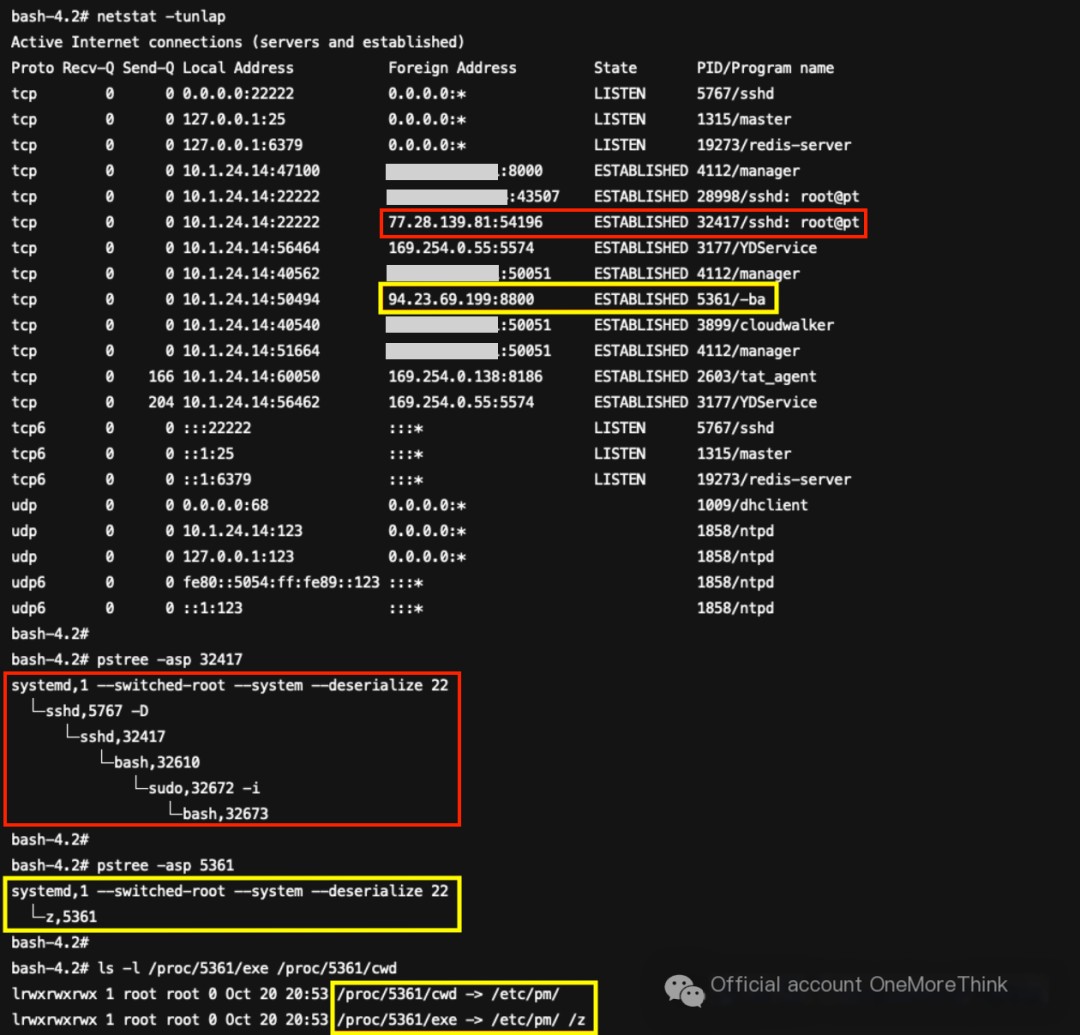
77.28.139.81 (North Macedonia) logged into SSH but did not execute any other commands. No further investigation is needed; kill the process associated with this connection.
94.23.69.199 (France) has no parent process and is executing the malicious program /etc/pm/ /z. Kill the process associated with this connection and delete the malicious program.
/etc/pm/ directory, /etc/pm/’ ‘/z file
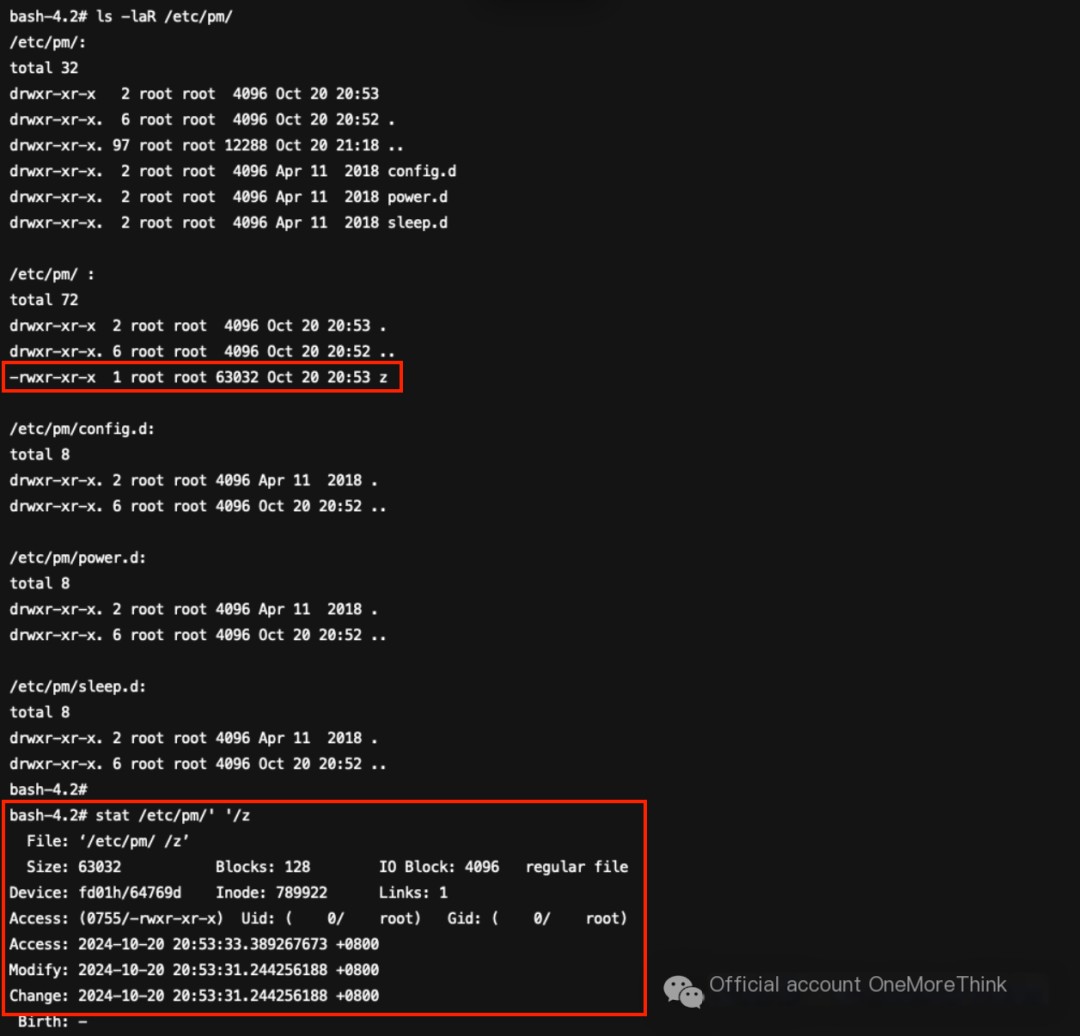
Kill the malicious process and delete the malicious program.

3.3 Muyun HIDS: Removing Malicious Programs Associated with /etc/xdg/’ ‘/.cm/z Alert
/etc/xdg/ directory

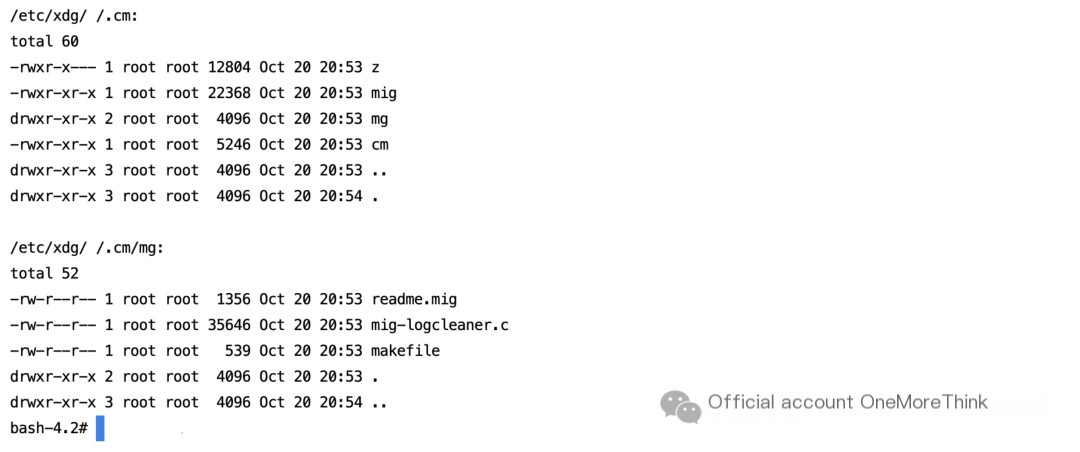
/etc/xdg/’ ‘/.cm/mig file, /etc/xdg/’ ‘/.cm/z file
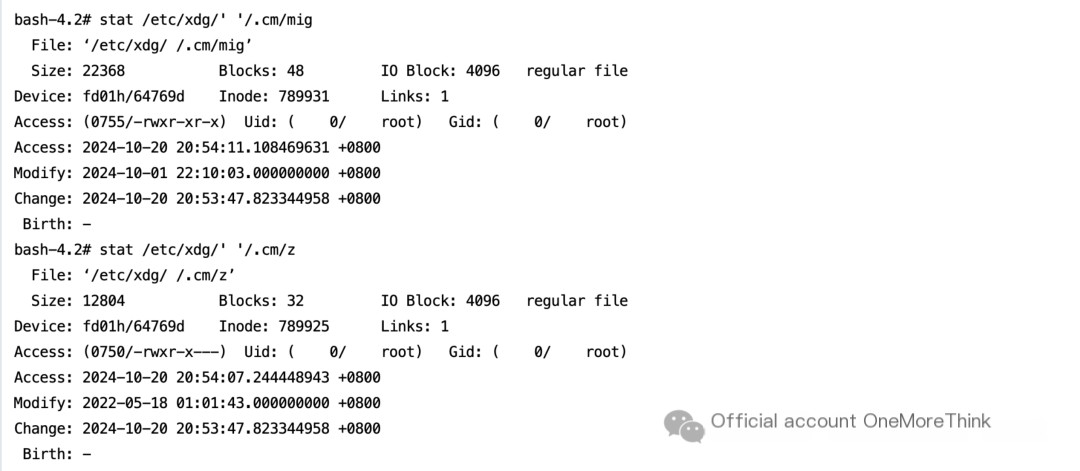
Delete the malicious program.

3.4 Delete Malicious Program Related to Alert /etc/udev/’ ‘/.c/init
/etc/udev/ directory
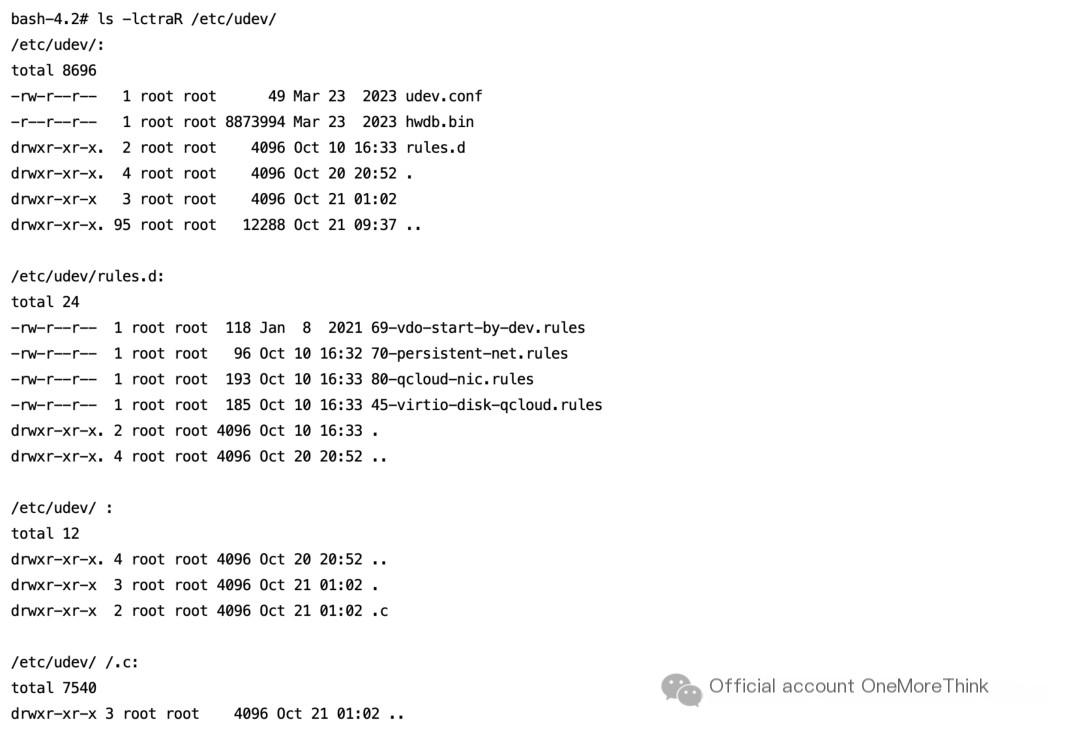
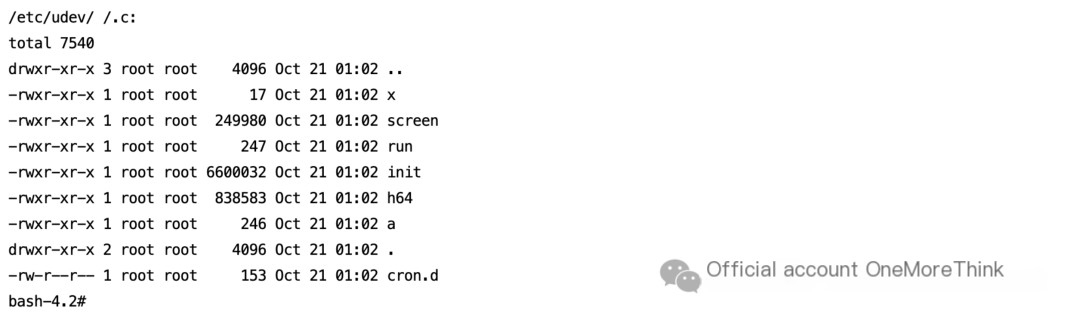
/etc/udev/’ ‘/.c/init file
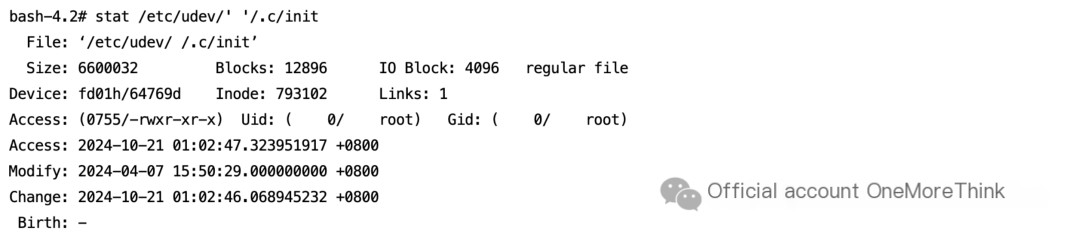
Delete the malicious process.

3.5 Delete Malicious Program Related to Alert /etc/X11
/etc/X11/m directory. The /etc/X11/.lans/scan2 file was not found.
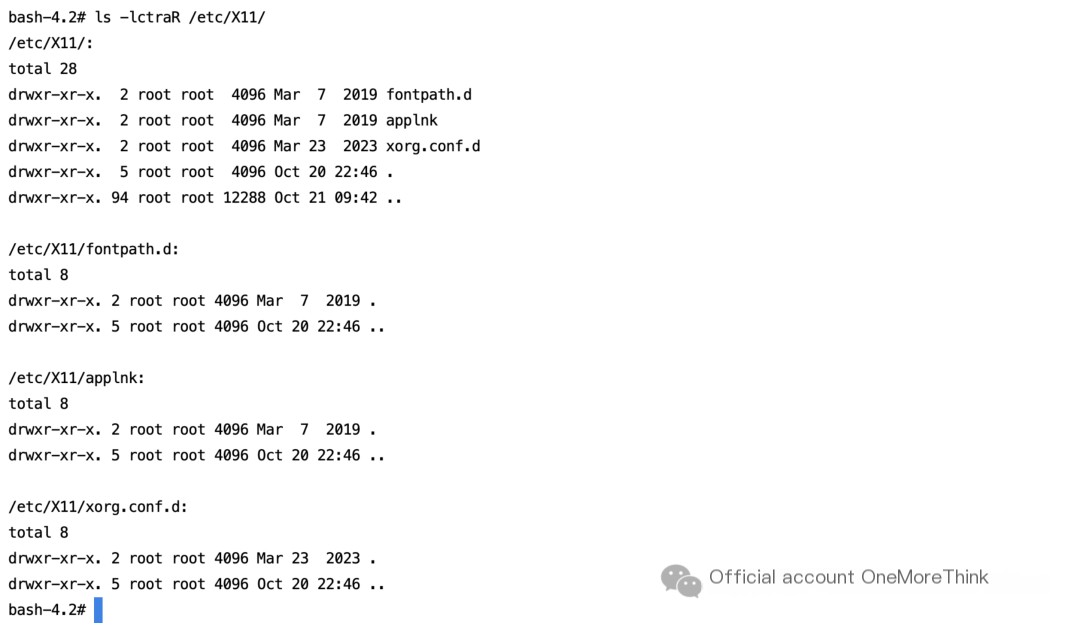
Delete the malicious file.

3.6 Delete Time-Related Malicious File /tmp/resolv.conf
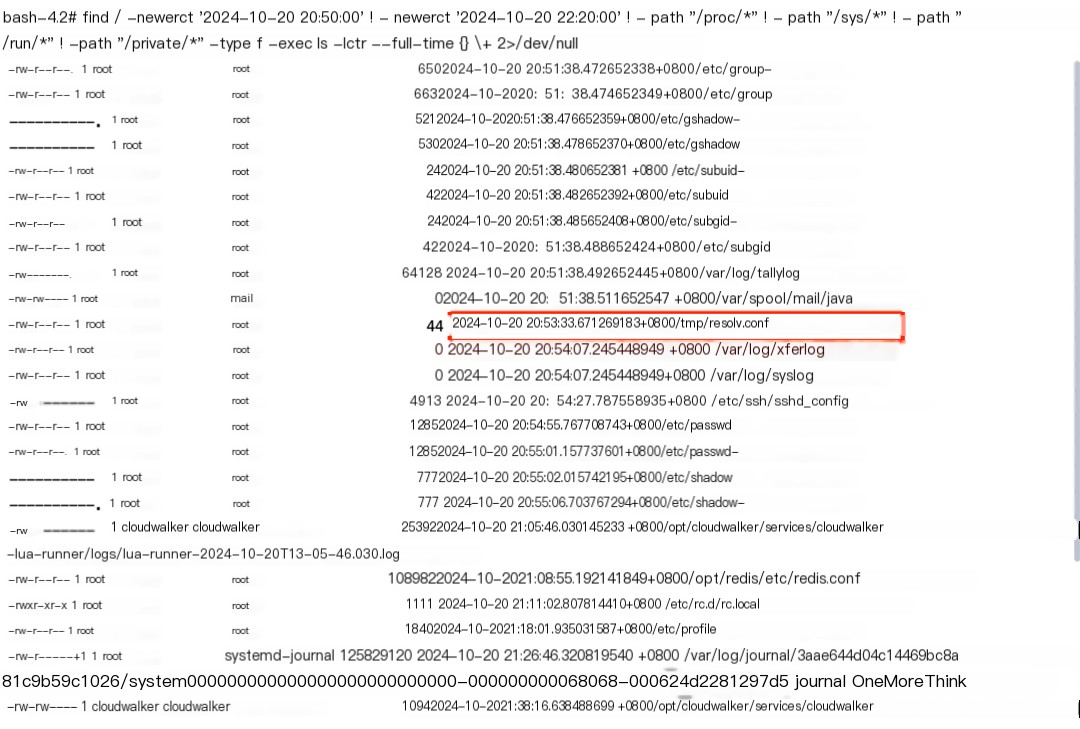
It was discovered that the attacker configured a DNS server that resolves malicious domain names; this needs to be deleted.

4. Eradication
4.1 Clean Up System User Backdoors
A new user, “java,” was discovered.
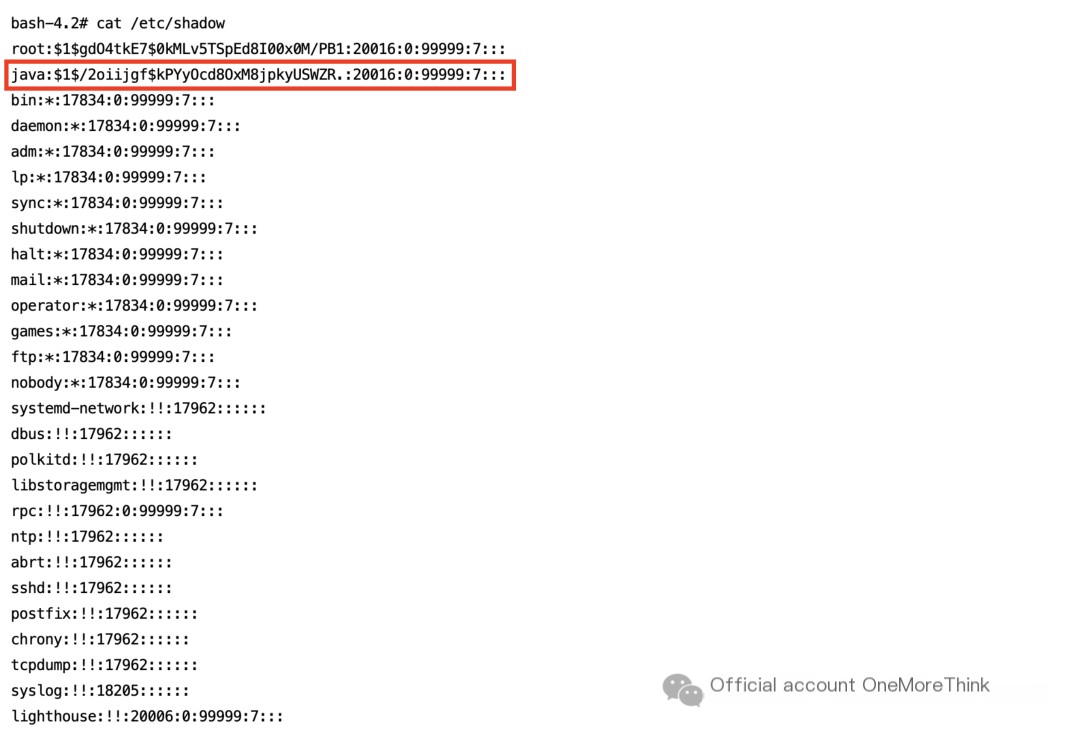
Delete the “java” user.

The root user’s password was changed by the attacker, resulting in an inability to log in. The password needs to be changed.

4.2 Harden Weak Password Vulnerabilities
Since the server only has the SSH service open, and only the root user can log in, it is suspected that the root account was compromised due to a weak password. The weak password needs to be changed.
Note: The /var/log/secure log was deleted, and Muyun HIDS disabled brute-force detection due to too many alerts.
5. Recovery
5.1 Restore Root User Login
See section 4.1.
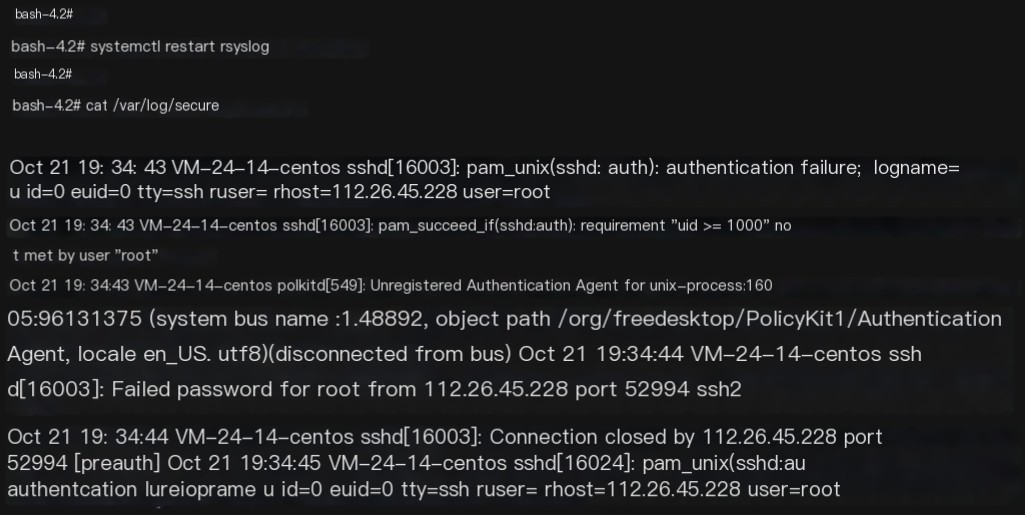
5.2 Restore Secure Log Recording
Upon inspection, it was found that the /var/log/secure log recording function was disabled.
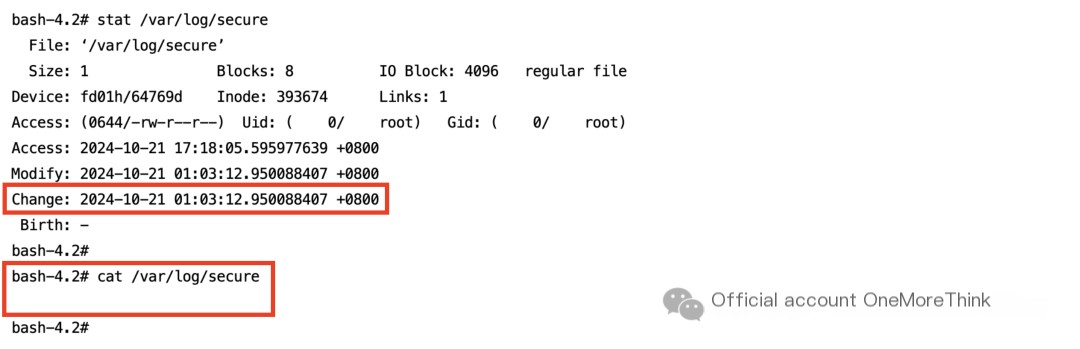
Restarting the service resolves this issue.
6. Follow-Up
6.1 Remote Log Storage
Because logs on the server can be deleted by attackers, preventing attack path tracing, consider sending logs to a remote server for storage.


