In the face of the increasingly vast network now, our corporate networks establish firewalls between the corporate network and the internet in order to achieve relative security. However, in some circumstances, firewalls may not function effectively.
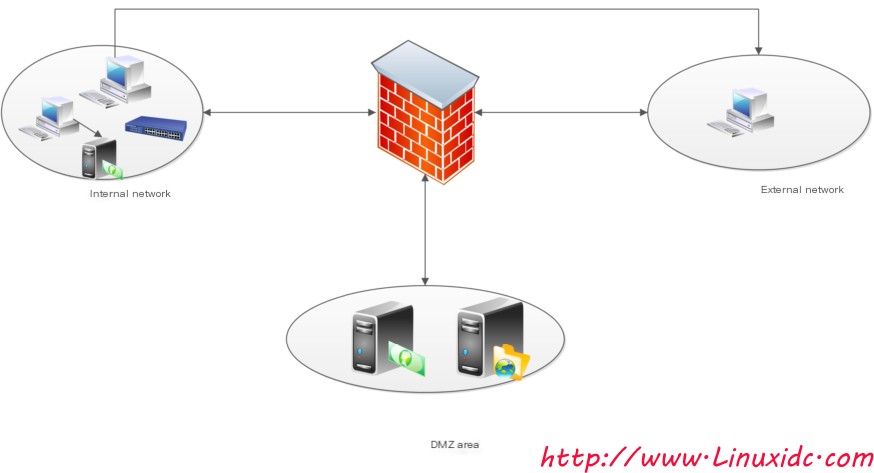
As shown in the picture above:
The DMZ area where the enterprise’s internal network, external network, and server are located
(1) Attacks from enterprise internal network users
(2) Internal network users bypass the firewall to access the internet, are attacked, and consequently, attackers attack the internal network
(3) Attackers implement attacks through viruses, Trojans…
At this time, some strategies are needed for monitoring, allowing us to detect abnormalities in the network promptly and take remedial actions. Early IDS (Intrusion Detection System) was used for monitoring. Later, it evolved into IPS (Intrusion Prevention System), which further allows monitoring and taking actions to block certain attacks upon detecting anomalies.
IDS Classification:
HIDS: Software-based, host-based (for example, Sessionwall and Snort, which we will discuss today)
It is installed on the protected host, but considering the cost, we cannot install such software on every host; thus, we prioritize installation on main servers.
Detection contents: (more detailed)
Application layer services, network traffic, logs, user behavior, whether important files have been modified.
NIDS: Hardware-based, network-based
Connects to a switch, receives data coming from the switch. However, to receive data from multiple hosts under the switch, port mirroring technology is needed. This requires deploying NIDS on each switch. However, if the network is too large, this approach can be costly.
Later, RSPAN (Remote Switched Port Analyzer) was introduced, allowing detection of data information from other switches.
Detection contents: (not detailed enough)
It can only detect up to the fourth layer of the network’s 7-layer structure, unable to detect application layer services, viruses…
Therefore, in practical network applications, these two defense systems are often used in combination: HIDS on important servers and NIDS on other hosts.
IDS Operation Principle:
 >
>
If it is an IPS, it will take further actions to block attack behaviors.
The open-source intrusion detection system Snort has, to date, evolved into a powerful network intrusion detection/prevention system (NIDS/NIPS) with features such as multi-platform, real-time traffic analysis, and network IP packet logging. Snort complies with the GNU General Public License (GPL), and Snort is based on libpcap.
Snort has three modes: sniffer, packet logger, network intrusion detection system. Sniffer mode only reads packets from the network and displays them continuously on the terminal. Packet logger mode logs the packets to the hard drive. Network intrusion detection mode is the most complex and configurable, allowing Snort to analyze network traffic to match user-defined rules and take certain actions based on detection results.
Snort deployment is highly flexible and can run on many operating systems, such as Windows XP, Windows 2003, Linux, etc. However, considering the security and stability of the operating system platform and requirements for working in conjunction with other applications, if the intrusion detection system itself is unstable and easily attacked, it cannot effectively detect other security vulnerabilities. In comparison between Linux and Windows operating systems, Linux is more robust, secure, and stable. Snort’s functionality is enhanced mainly through the collaborative work of various plugins, so selecting suitable databases, web servers, graphic processing software, and versions is very important when deploying. Snort is generally deployed with a three-layer structure: sensor layer, server layer, and administrator console layer. The sensor layer is a network packet sniffer layer, collecting network packets and handing them over to the server layer for processing. The administrator console layer mainly displays detection and analysis results. Snort can be deployed using a three-layer structure for large enterprise networks or integrated into a single machine, or using a two-layer structure by integrating the server layer and console.
For more details, continue to read the exciting content on the next page: http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-11/92260p2.htm
More about Snort: Click hereDownload Snort: Click here
Related Reading:
Snort + Base Intrusion Detection Configuration http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-02/79805.htm
Installing Snort on Ubuntu 12.04 Details http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2013-01/78554.htm
Snort Enterprise Deployment Practice http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-08/68946.htm
Setting up IDS Intrusion Detection System with Snort+base http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-08/67865.htm
Linux Platform Snort Intrusion Detection System Practical Guide http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-08/67048.htm
From Compilation, Installation to Debugging Snort under Ubuntu http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2011-09/44157.htm
3. Integrate PHP and MySQL
Install the necessary packages
Libpcap (packet capture library), mysql (stores captured data), apache (web server), php (web scripting language), adodb (provides database support for php), and base (Basic Analysis and Security Engine)
Set the Linux host network to connect to the internet
Configure the Yum environment
vim /etc/yum.repos.d/rhel-debuginfo.repo

Mount the optical disc

Install the necessary packages
yum install php php-gd php-pear php-mysql mysql-server httpd libpcap -y
Open the service and set it to start on boot
service httpd start
chkconfig httpd on
service mysqld start
chkconfig mysqld on
Set a password for mysql
mysqladmin -u root -p password ‘123’
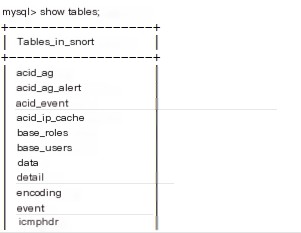
Set up the database for capturing data and import the template


4. Due to the low version of pear, it needs an online upgrade

Upgrade
pear upgrade pear
Install graphical modules
pear install Image_Graph-alpha Image_Canvas-alpha Image_Color Numbers_Roman Mail_Mime Mail
5. Handle base (physical directory access)
tar -zxvf base-1.4.5.tar.gz -C /var/www/html/
mv base-1.4.5/ base
cd /var/www/html
chmod o+w base
Thus, it can be accessed directly via http://***/base
6. Handle adodb
unzip adodb514.zip
mv adodb5 /var/www/html/adodb
cd /var/www/html/base
Copy graphical image tools
cp world_map6.png world_map6.txt /usr/share/pear/Image/Graph/Images/Maps/
7. Access
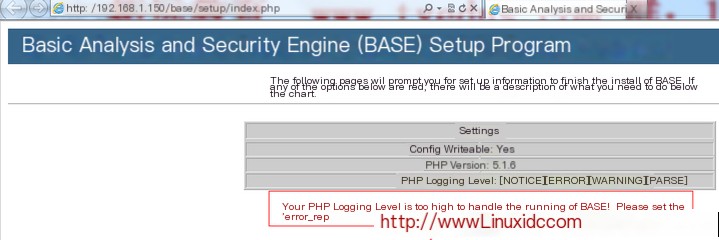
It prompts us that the PHP log level is too high, and it also provides our solution
vim /etc/php.ini
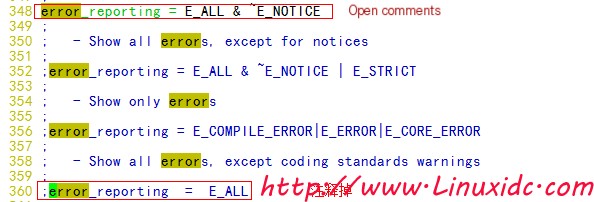
Restart apache
service httpd restart
Access again
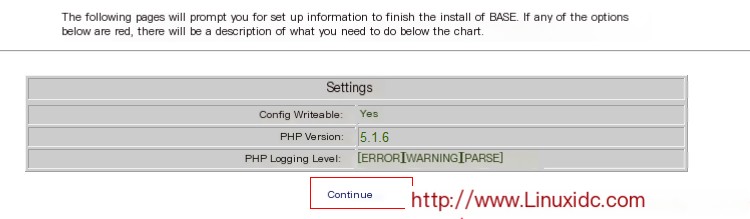
Proceed to the next step
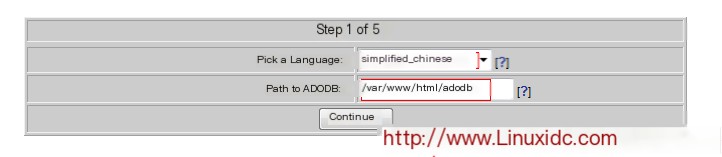
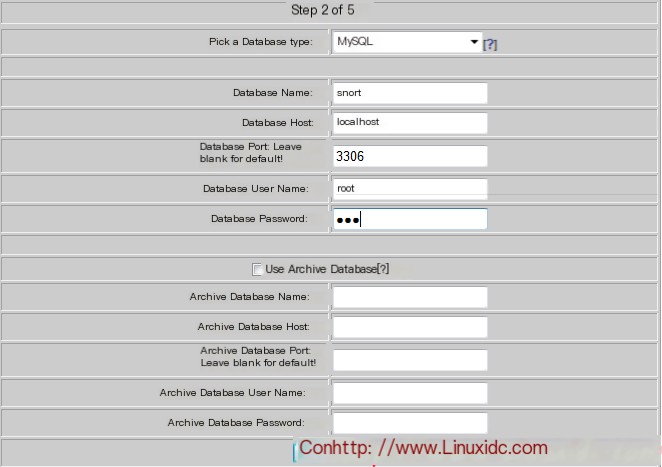
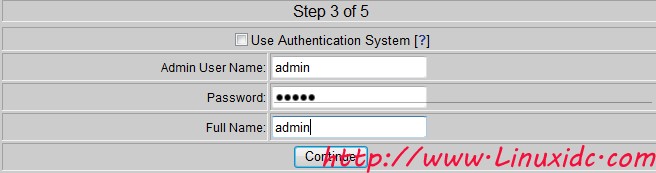


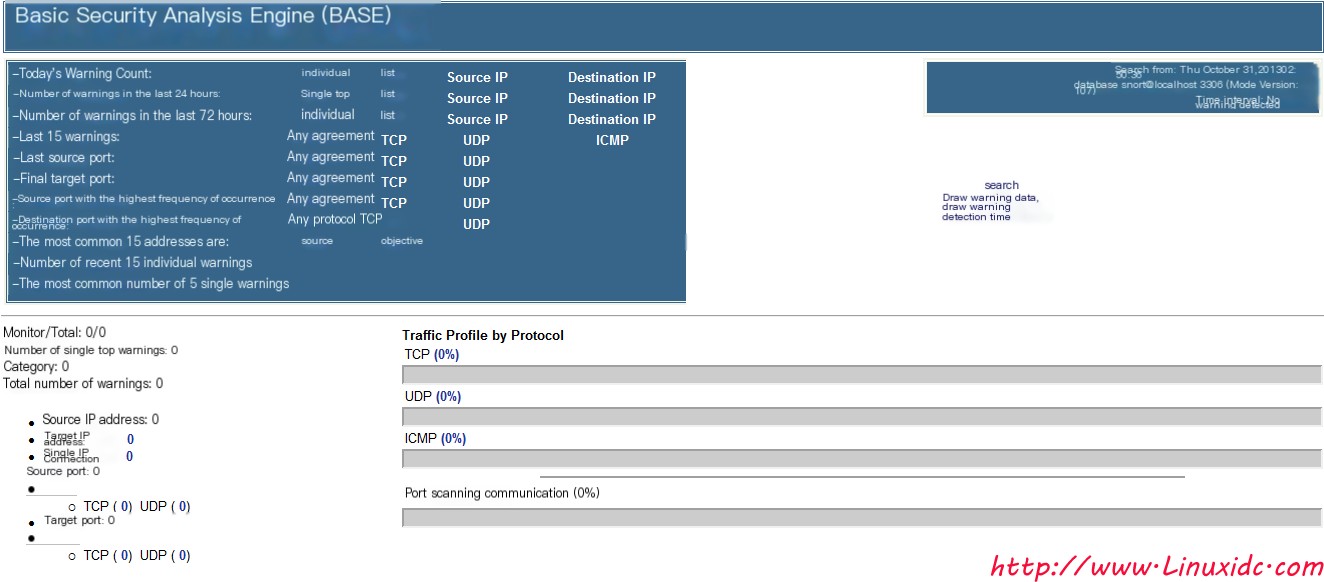
At this time, the monitoring screen appeared, but there was no data. This is because we did not tell it to deliver the captured data to the MySQL database.
8. Install the software packages for connecting Snort and BASE
rpm -ivh snort-MySQL-2.8.0.1-1.RH5.i386.rpm
Declare to deliver captured data to the MySQL database
vim /etc/snort/snort.conf

Set it to record only those alerts of level (and above)
9. Implement data capture
snort -vde -c /etc/snort/snort.conf &>/dev/null &
Access again
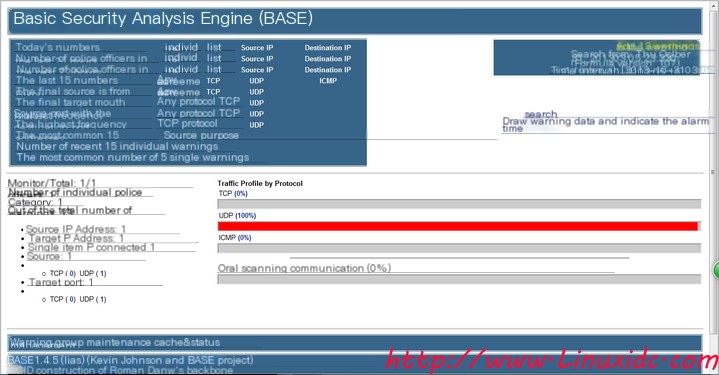
We can see that information has been recorded, and thus, real-time network monitoring can be achieved.


