Contents
hide
Introduction to Network Information Security: An Overview of Computer Network Security
I. Basic Concepts of Network Security
1. Definition of Network Security
- Security, as defined in the dictionary, refers to measures taken to prevent espionage or deliberate sabotage, crime, and assaults.
- Network security refers to a comprehensive set of measures taken to protect computer network hardware, software, and data from accidental or intentional destruction, alteration, eavesdropping, impersonation, leakage, unauthorized access, and to ensure the continuous and effective operation of network systems.
- The scope of network security protection includes: cybersecurity, computer system security, network security, and information security.
2. Objectives of Network Security
- Reliability is the fundamental premise for the normal operation of all information systems, generally referring to the feature of completing specified functions under specified conditions and within specified timeframes.
- Confidentiality refers to the characteristics of an information system that prevents unauthorized information leakage; information is limited to authorized users. Confidentiality is mainly achieved through information encryption, identity authentication, access control, and secure communication protocols, with encryption being the most fundamental measure to prevent unauthorized information leakage.
- Integrity refers to the property that information cannot be altered without authorization. While confidentiality emphasizes preventing unauthorized disclosure, integrity focuses on ensuring that information cannot be modified, deleted, forged, added, damaged, or lost during storage and transmission. The information must retain its original form throughout storage and transmission. Information integrity indicates the reliability, correctness, effectiveness, and consistency of the information, and only intact information is trustworthy.
- Availability refers to the characteristic that allows authorized users to access information resources as needed. Availability is a security feature of information systems oriented toward user service. Only by remaining continuously available can information systems allow authorized users to access the services provided at any time and from any location based on their needs.
- Controllability is the characteristic referring to the ability of an information system to control the content and transmission of information.
- No-Repudiation, also known as non-repudiation, means that parties in communication cannot deny or repudiate completed transactions and commitments. Digital signatures are used to prevent parties from denying having sent or received information.
- The ultimate goal is to achieve network information system reliability, confidentiality, integrity, availability, controllability, and no-repudiation through various technological and administrative means.
3. Network Security Model
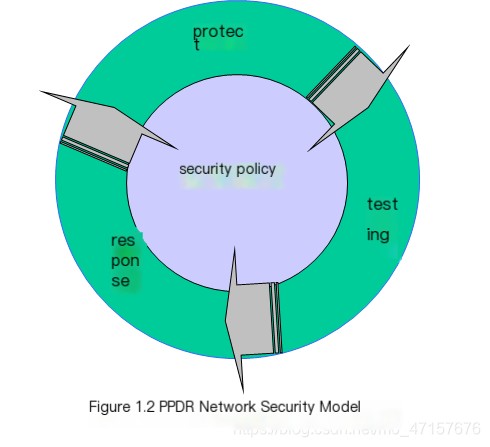 >
>
4. Network Security Policy
- Network security policy is the guiding document for ensuring the security of institutional networks.
- Security Policy Principles
- Balance Principle: Network security policies need to maintain a relative balance between security requirements, usability, efficiency, and security costs. Scientifically developing balanced network security policies is crucial for improving investment returns and maximizing network efficiency.
- Timeliness Principle: Due to the ever-changing factors affecting network security, network security issues are characterized by their significant timeliness.
- Minimization Principle: The more services provided by a network system, the more security vulnerabilities and threats there are. Therefore, network services not specified in the security policy should be disabled; user permissions should be minimally configured to meet security policy definitions; unnecessary accounts and host trust relationships should be promptly deleted to minimize threats to network security.
- Security Policy Content
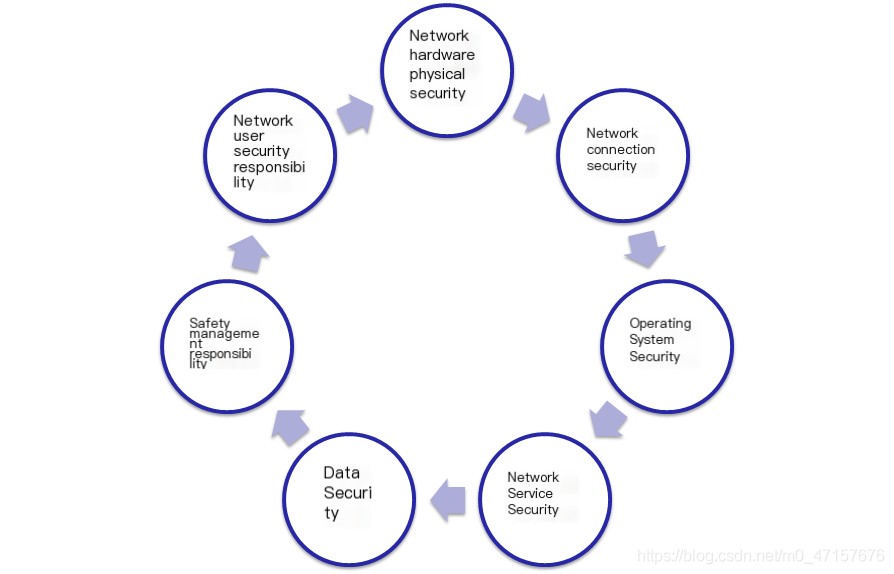 >
>
II. Network Security Vulnerabilities and Threats
1. Software Vulnerabilities
- Software Vulnerability refers to security risks caused by not considering abnormal inputs or errors in coding during software design and development. Software vulnerabilities are also known as software vulnerabilities or bugs.
- The main reason for software vulnerabilities is that software designers cannot consider all inputs thoroughly. Software vulnerabilities are an objective fact existing in any software. Before official release, software products generally undergo alpha, beta, and gamma releases for repeated testing in order to minimize software vulnerabilities.
2. Network Protocol Vulnerabilities
- Similar to software vulnerabilities, it refers to security risks caused by incomplete network communication protocols. To date, security risks have been identified in almost all protocols of the TCP/IP protocol suite widely used on the Internet.
3. Security Management Vulnerabilities
- Network security management involves a series of network security measures taken under the guidance of network security policies to protect the network from internal and external threats. Network security policies are rules that must be followed based on network security objectives and the network application environment to provide specific levels of protection.
- Network security is relative, based on trust, and absolute network security never exists.
4. Sources of Network Threats
- External attacks aimed at stealing network information are generally referred to as passive attacks, while other external attacks are collectively referred to as active attacks. Passive attacks primarily compromise information confidentiality, while active attacks primarily compromise information integrity and availability.
- Active attacks mainly come from network hackers, hostile forces, network financial criminals, and commercial competitors. The term “hacker” originally had no negative connotation, referring to computer enthusiasts who are independent thinkers, exceptionally intelligent, energetic, and passionate about exploring software mysteries and showcasing personal talent. Domestically, the term hacker is often used pejoratively to refer to malicious attackers who exploit network security vulnerabilities to deliberately compromise information resource confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
This article participates in the Tencent Cloud Media Synchronization Exposure Plan, sharing content from the author’s personal site/blog. Originally published: 2020/10/18. For infringement claims, please contact [email protected] for removal. Visit to view hackerssecuritynetwork securitysecurity vulnerabilities.“`


